Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) Enhancement for vSAN Stretched Cluster
Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) Enhancement for vSAN Stretched Cluster
VMware vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) automates the initial placement of virtual machines and workload balancing across a vSphere cluster. DRS also makes cluster maintenance easier by streaming the migration of virtual machines to and from hosts as each host enters and exits maintenance mode. These capabilities help ensure uptime, reduce manual efforts, and avoid compute resource contention. DRS works with a wide variety of shared storage solutions including VMware vSAN. This includes vSAN standard clusters, 2-node clusters, and stretched clusters.

vSphere 7 Update 2 and vSAN 7 Update 2 include enhancements that further improve interoperability between DRS and vSAN Stretched Clusters. Prior to Update 2, DRS might prematurely migrate virtual machines back to their original location after a site failure regardless of whether data is fully synchronized between the two sites. The improvements to DRS in Update 2 prevent the migration of a virtual machine until its data is synchronized. DRS is now aware of the vSAN Stretched Cluster configuration and this article will cover in detail the following topics:
- What is needed to enable the vSAN aware DRS enhancement in your cluster and are there any recommendations?
- How does the enhanced DRS work?
- What are the improvements in terms of performance for your Stretched Cluster configuration?
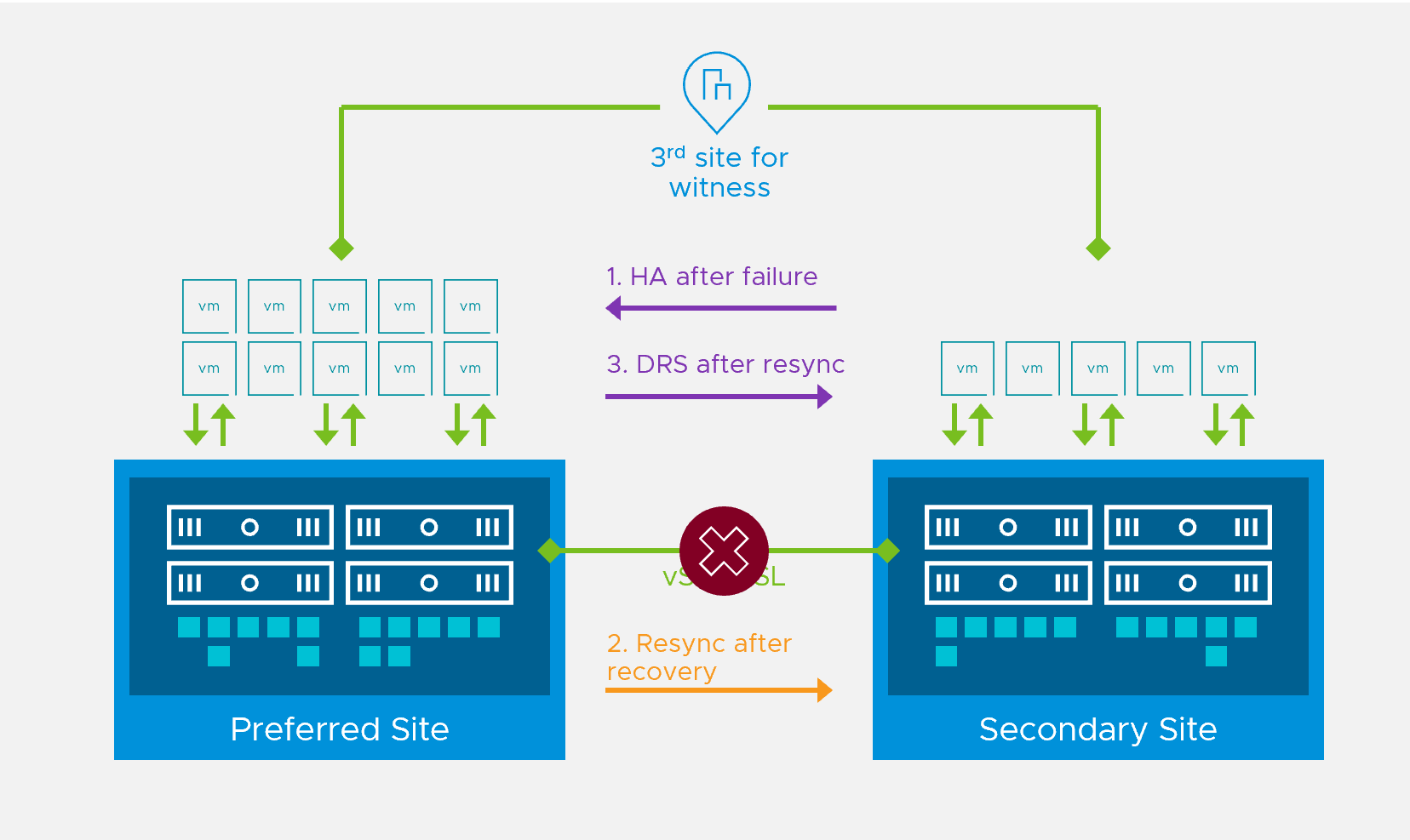
How Does the Enhanced DRS Work?
Before vSAN 7 Update 2
vSAN Stretched Cluster provides an automated method of moving workloads within the two fault domains. In case of full site failures, VMs are restarted on the secondary site by vSphere HA. This minimizes downtime for critical production workloads. Once the primary site is back online, DRS immediately rebalances the VMs back to the primary site with soft affinity rules. This process could cause the VM to read from the secondary site while the VM’s data components are still rebuilding, which temporarily increases the I/O crossing the inter-site link.
With vSAN 7 Update 2
vSphere’s DRS, tightly integrated with vSAN Update 2, introduces a fully automated read locality solution for recovering from failures on a vSAN Stretched Cluster. The read locality information indicates the hosts the VM has full access to, and DRS uses this information when placing a VM on a host on vSAN Stretched Clusters. DRS migrates the VMs back to the primary site once the vSAN resynchronization is completed and the VM’s data components have achieved full read locality. This again, allows you to operate DRS in fully automatic mode in case of a site failure.
In case of partial site failures, if a VM loses read locality due to loss of data components equal to or greater than its Failures to Tolerate, vSphere DRS will identify the VMs that consume a very high read bandwidth and try to rebalance them to the secondary site. This way, we ensure that VMs with read-heavy workloads are not impacted during partial site failures. Once the primary site is back online and the data components have completed resynchronization, the VM is moved back to the site it is affined to.
Configure vSAN Aware DRS for Stretched Cluster and Recommendations
DRS awareness of vSAN Stretched Clusters is built into vSAN 7 Update 2. There is no need to make changes in configuration or operating processes. It works with all affinity rules. The recommendation with previous versions of vSAN was to set DRS Automation to Manual or Partially Automated. With vSAN 7 Update 2, this can be set to Fully Automated to get the most benefits from DRS with vSAN stretched clusters. You can find more details here.

To Conclude
DRS plays a vital role in the smooth uninterrupted life of the VMs, and the cluster balance in vSAN. DRS’s logic has been previously improved to be workload-centric and relies on VM DRS score to achieve better results in terms of optimization and performance. With vSAN 7 Update 2, DRS continues to evolve in the same direction, and unlike other stretched storage solutions, DRS is ‘aware’ of the data synchronization activity across a vSAN stretched cluster. This helps ensure optimal performance when recovering from a site outage.
