DataStax Enterprise on VMware vSAN Deployment Options
VMware and DataStax
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Ready, Enterprise-grade Availability, Simplified Management
Organizations are leveraging modern data platforms, such as Apache CassandraTM, to power new products and services across industries. For example, Cassandra empowers retailers to provide an omnichannel shopping experience with tailored customer experiences in real time. However, the implementation and ongoing management operations can be a significant barrier to adoption. Organizations are betting their growth on distributed technologies, and they want a scalable full-stack solution that is always available, secure, and simple to deploy and manage.
VMware® and DataStax have partnered to build a hybrid and multi-cloud solution designed to meet the data and availability requirements of the most demanding applications with built-in high availability and failure protection across availability zones, regions, data centers, and clouds in three of the four largest public cloud providers: Amazon, Microsoft, and IBM, as well as a rich ecosystem of hundreds of public cloud providers globally.
Our joint integration simplifies operations and eliminates data and application silos with consistent processes and tooling while offering intrinsic security for both data-at-rest and in-flight software-based encryption that meets strict U.S. federal government standards. DataStax and VMware’s hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) combined with support for on-premises and VMware Cloud enable organizations to manage both traditional and cloud-native applications with the same interface delivering vast efficiency gains and consolidation benefits, greater consolidation ratios, a single management toolset, and automated lifecycle management, to name a few.
VMware HCI
An Ideal platform for cloud-native applications
- Predictable and performant infrastructure: Cloud-native apps tend to scale linearly, and HCI’s ability to add both compute and storage resources incrementally more precisely matches resources to needs as the application expands.
- Unified Management: HCI provide an ideal platform to manage compute and storage resources for virtual machines as well as containers. VMware HCI uses the same tools to manage cloud-native apps that system admins use to manage their VM environments today.
- Lower-cost, high-performance infrastructure: On the CAPEX side, customers have reported savings up to 75% versus traditional three-tier, all-flash arrays with fiber channel networking. On the OPEX side, hyperconverged infrastructure simplifies operations by prolific use of automation studies have shown the management OPEX is up to 58% lower with HCI versus traditional all-flash arrays.
Agility through Storage Policy Based Management (SPBM)
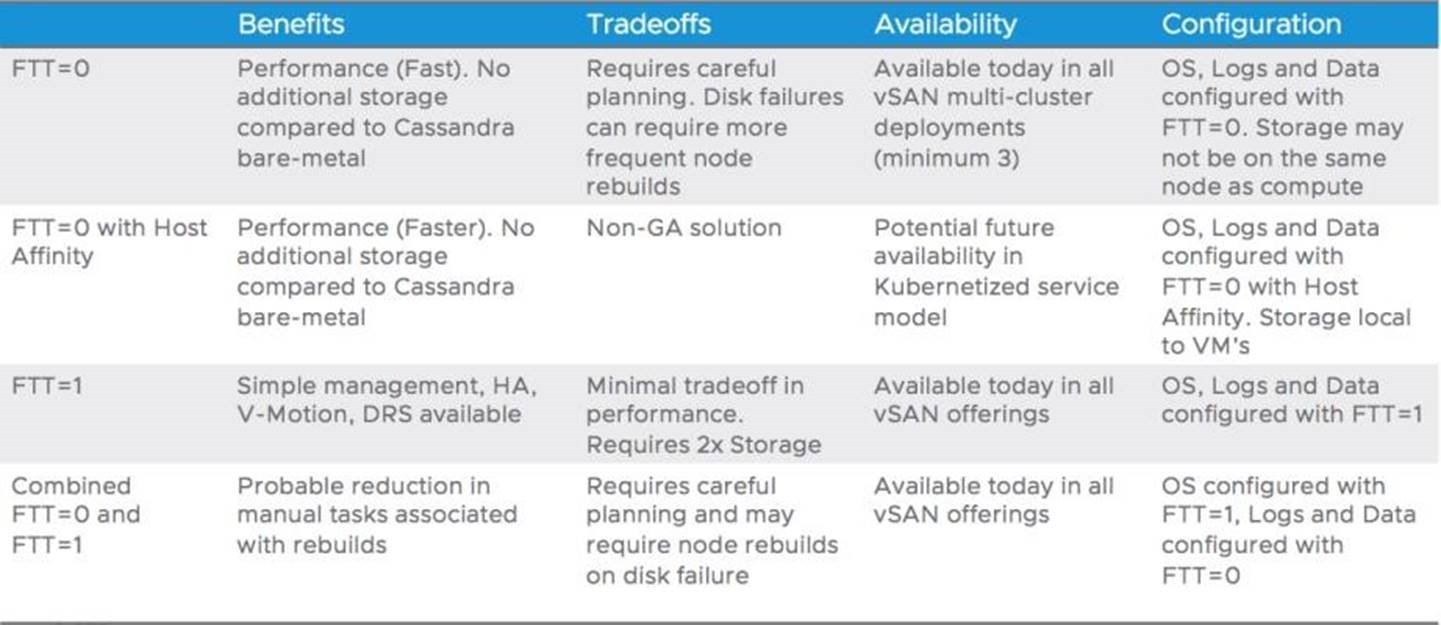
VMware vSAN™ was built around the idea of assigning storage-related settings on a per-VM basis, or even per-virtual disk basis. Administrators can be prescriptive to the specific application needs, based on its role in the data center. They can easily increase the level of failures to tolerate on VM OS disk and log disk, while applying policies for data disks running DataStax Enterprise (DSE), which allows for a level of control that is not possible with other approaches. Administrators can assign key availability and performance capabilities via policy. For instance, the Failures to Tolerate (FTT) capability addresses the key customer and design requirement of availability. With FTT, availability is provided by maintaining replica copies of data to mitigate the risk of a host failure resulting in lost connectivity to data or potential data loss. The FTT policy works in conjunction with VMware vSphere® High Availability (HA) to maintain availability.
|
|
Copies of Data on vSAN |
|
FTT=0 |
1 |
|
FTT=1 |
2 |
|
FTT=2 |
3 |
DSE Replication
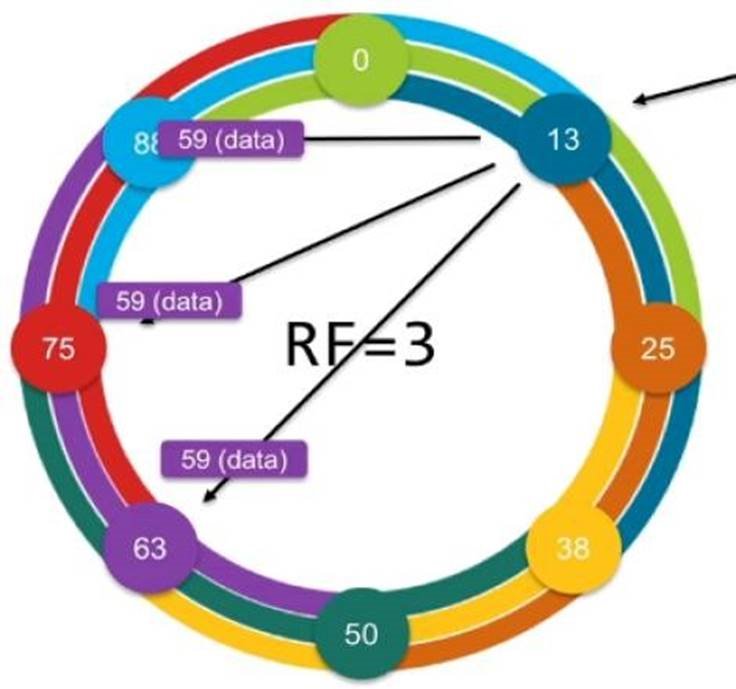
DSE uses racks so that no replica is stored redundantly inside a rack, ensuring replicas are spread throughout different racks in case one rack went down.
We leverage rack-aware snitch to ensure that multiple replicas are not stored on DSE nodes of the same VMware ESXi™ host. With the rack name in the cassandra-rackdc.properties file aligned to a physical chassis name, replicas will split across chassis for a given token.
DSE Rack Awareness
DSE uses racks so that no replica is stored redundantly inside a rack, ensuring replicas are spread throughout different racks in case one rack goes down.
We leverage rack-aware snitch to ensure that multiple replicas are not stored on DSE nodes of the same ESXi host. With the rack name in the cassandra-rackdc.properties file aligned to a physical chassis name, replicas will split across chassis for a given token.
Node Density
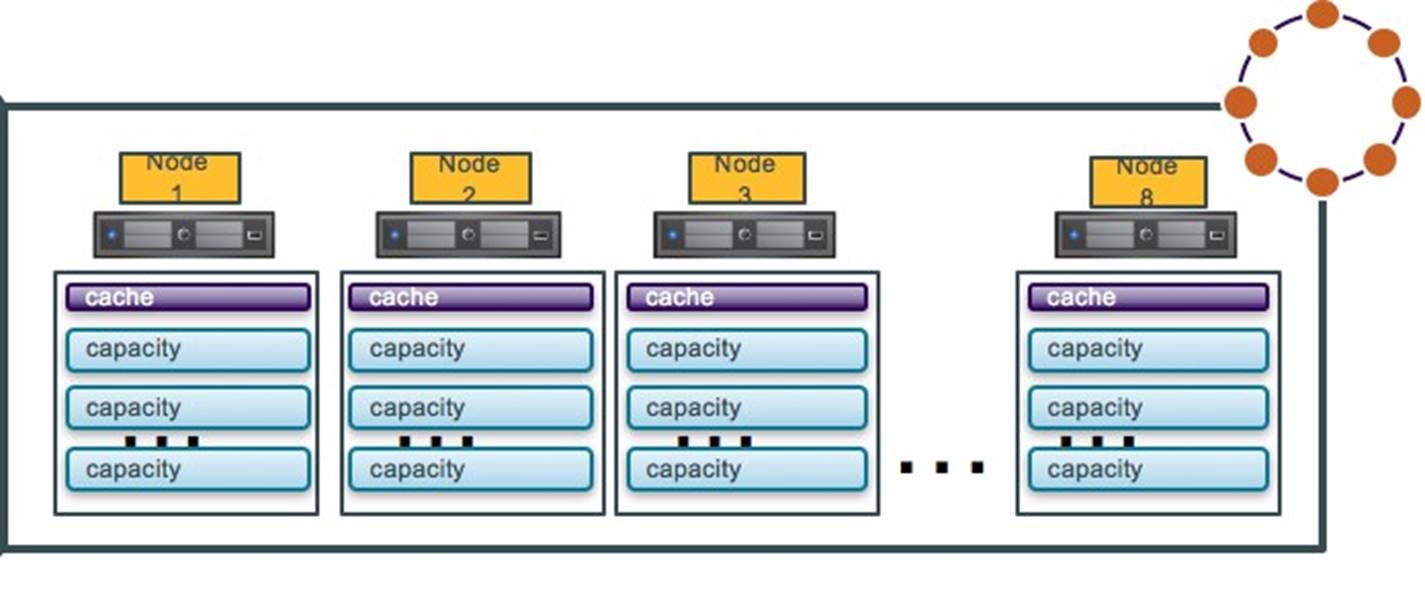
Option 1: One DSE Node per Host
In option 1, a DSE cluster is deployed on some ESXi hosts with equal or less than one DSE node per host. Running a DSE cluster in this configuration does not require any changes to the topology or rack configuration, the DSE node fully uses the computing and storage resource of the host, all deployment and operations are similar to the physical servers. There is no architecture change if customers are migrating their existing physical environment to a virtual environment.
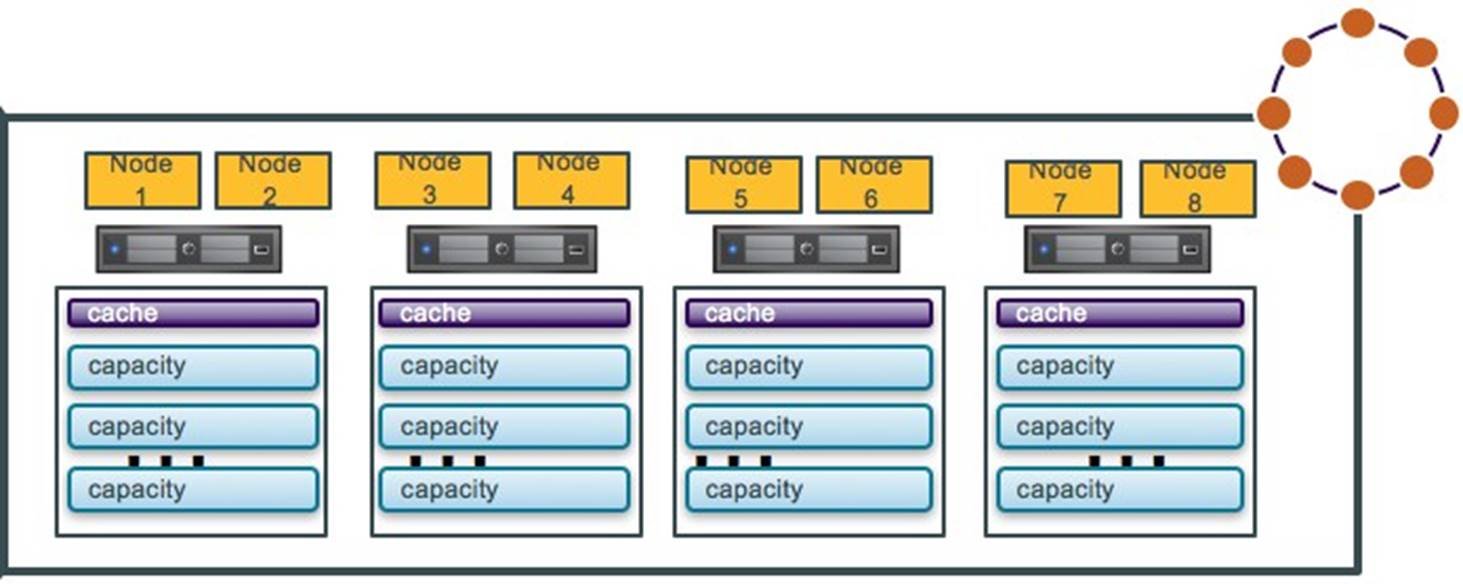
Option 2: Multiple DSE Nodes per Host
Option 2 shows multiple DSE nodes per host; it offers the server consolidation benefits and provides more flexibility for DSE cluster resource assignments. In this option, DSE rack-aware snitch needs to be configured to ensure DSE replicas are not placed on the same physical host.
Deployment
For small DSE cluster deployments, we use only one vSAN cluster for management and simplicity; for large deployments, multiple vSAN clusters is a feasible option.
See the following chart for various configurations in one vSAN cluster and multiple vSAN clusters.
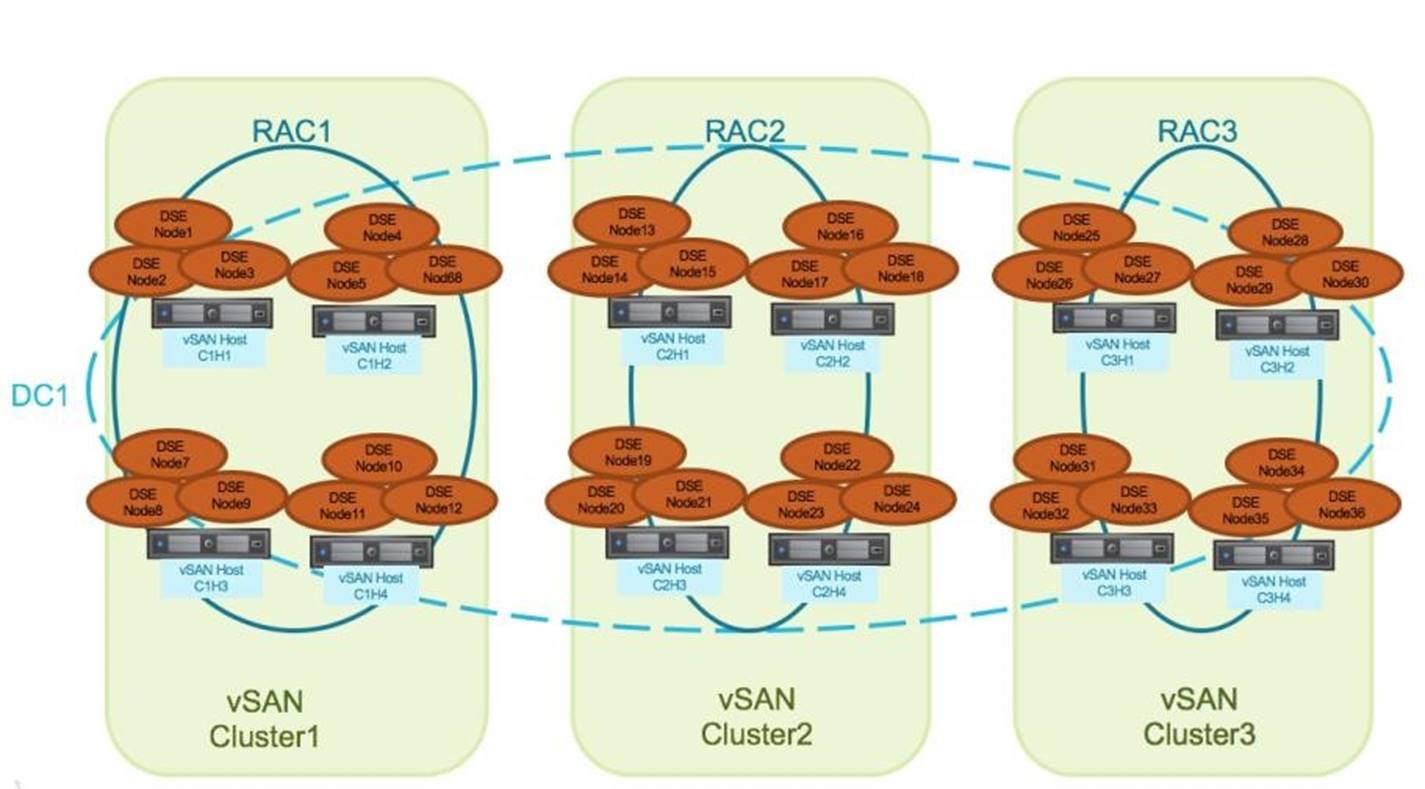
Multiple vSANCluster Deployment
As shown in the multiple vSAN cluster deployment diagram, we utilize DSE’s rack awareness, each DSE replica is stored in a different rack in case one rack went down, The commonly used DSE replication factor is 3, so it requires a minimum of 3 vSAN clusters to ensure DSE application availability without vSAN storage level protection.
vSAN FTT=0
Configure OS, logs, and data disks with FTT=0; and configure DSE nodes with discrete vSphere/vSAN clusters per DSE rack definition. This deployment is only available in multiple vSAN clusters, data locality is not required for data availability. Application-level availability is guaranteed by ensuring that DSE racks are aligned with vSAN clusters. It has no additional capacity requirements at the risk of single disk failures requiring replacing entire VM not just failed data VMDK. Disk failures can require more frequent node rebuilds. This deployment scenario requires careful management and will increase the number of virtual machines affected by capacity disk, cache disk, network, or host failures.
vSAN FTT=0 with Host Affinity
Configure OS, logs, and data disks with FTT=0.
This option reduces complexity and increases performance. Host Affinity pins the virtual machine’s data drives to the host it is running on, thus reducing additional storage overhead and improving performance. The Host Affinity feature is currently an RPQ feature and is not fully integrated with vSphere’s features such as VMware vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler™ and vSphere HA.
vSAN FTT=1
Configure OS, logs, and data disks with FTT=1. This option applies to both single vSAN cluster deployment and multiple vSAN cluster. It combines availability from both the vSphere stack and DSE’s built-in resiliency. it allows hypervisor and cluster-level activities such as snapshots, HA, and DRS to be fully aware and compatible with vSAN. Running DSE on vSAN with FTT=1 simplifies deployment while maintaining all operational functionality in the vSphere clusters. vSAN is self-healing and will attempt to re-establish full storage protection compliance with the expected limited performance impact to the application. It performs the resynchronization actions automatically, all while maintaining a fair balance of resynchronization and guest VM traffic to ensure that DSE can maintain sufficient levels of performance during failure recovery. Applications benefit from vSAN’s storage-level protection and vSphere HA’s automated recovery from host failures.
Combined FTT=0 and FTT=1
Configure OS disk with FTT=1, configure logs and data disks with FTT=0; and configure DSE nodes with discrete vSphere/vSAN clusters per DSE rack definition.
This option is a blend of availability and capacity savings, single hardware failure will not affect VM availability. Single permanent disk failure means some data VMDKs will need to be recreated followed by DSE disk replacement methodologies. This option requires careful planning and the failure recovery may require node rebuilds on disk failures.
Agility Personified
- Adopt and integrate the very latest hardware technologies like 3D XPoint NVMe devices into a cluster.
- Scale up or out incrementally, as needed by an organization.
- Maintain full independence of storage from demands of other clusters. Just as with compute and memory, vSAN storage is a cluster resource that remains independent from other clusters.
Takeaway
SE contains application-level resilience through replication, and the enterprise-class resiliency features within vSAN provides user flexibility for various application needs. User customizable, storage-level resilience is built directly into vSAN, and is suitable for even the most demanding requirements.
The architecture of VMware vSAN allows it to address agility, consistent performance, scalability, and resiliency requirements that are top needs for data center administrators and application owners alike. Whether the DSE deployments are part of a large and coordinated deployment for a targeted set of applications, or a smaller scale deployment, vSAN provides operational simplicity and flexibility to meet the demands of customers’ modern application services. VMware vCloud Hybrid Service is an infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) offering operated and managed by VMware, with two class-of-service alternatives.
Learn more about
- Reference Architecture—Datastax Enterprise on VMware vSAN 6.7
- VirtualBlocks—VMware’s blog site for all topics related to storage and availability
- StorageHub—The one-stop location for all documentation on storage and availability
