Modernizing SQL Server 2019 Workloads with VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail
Executive Summary
Business Case
With the rise of modern applications, enterprises are facing new challenges to build, deploy, and manage containers, Kubernetes, and microservices architectures. Those modernized components must often work with the existing non-containerized application and stateful workloads like databases. In addition, when IT operators struggle to deliver the benefits of the cloud model, application teams seek more agile infrastructure in the public cloud, leading to the use of multiple clouds across on-prem and off-prem with drastically different infrastructure and operations. Managing such heterogeneous architecture while adhering to enterprise policies and security is a complex task for both IT operators and developers.
VMware Cloud Foundation™ provides a ubiquitous hybrid cloud platform for both traditional business critical applications and modern applications. It is built on VMware’s leading and proven software-defined stack including VMware vSphere™, VMware vSAN™, VMware NSX-T™ Data Center, VMware vRealize® Suite. VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu™ provides end-to-end security for compute, storage, network, Kubernetes management and cloud management. The result is agile, reliable, efficient cloud infrastructure that offers consistent operations across private and public clouds. VMware Cloud Foundation also contains built-in automated lifecycle management to simplify the administration of the software stack, from initial deployment to patching and upgrading.
Dell EMC VxRail™, powered by Dell EMC PowerEdge server platforms and VxRail HCI System Software, features next-generation technology to future proof your infrastructure and enables deep integration across the VMware ecosystem. Advanced VMware hybrid cloud integration and automation simplifies the deployment of a secure VxRail cloud infrastructure.
VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail, the Dell Technologies Cloud Platform, builds upon native VxRail, and VMware Cloud Foundation capabilities with unique integration features jointly engineered between Dell EMC and VMware that simplify, streamline, and automate the operations of your entire SDDC from Day 0 through Day 2 operations. The full stack integration with VMware Cloud Foundation on VxRail allows both the HCI infrastructure layer and VMware cloud software stack lifecycle to be managed as one complete, automated, and turnkey hybrid cloud experience, significantly reducing risk and increasing IT operational efficiency. This solution also allows us to perform cloud operations through a familiar set of tools, offering a consistent experience, with a single vendor support relationship and consistent SLAs across all your traditional and modernized workloads, public and private cloud, as well as edge deployments.
In this solution, we demonstrate reference architectures, planning and designing guidance, validation results and best practices for enterprise IT operators and developers to run both traditional mission-critical SQL Server workloads in virtual machines together with modernized SQL Server workload in containers on top of VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu platform on Dell EMC VxRail.
Business Values
Here are the top six benefits of deploying modernized SQL Server in a VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail environment:
- Full stack integration: Both the HCI infrastructure layer and VMware Cloud Foundation software stack lifecycle are managed as one complete, automated, and turnkey hybrid cloud experience that greatly reduces risks and increases IT operational efficiency.
- Automated Kubernetes infrastructure deployment: Enable organizations to run traditional workloads alongside cloud native container-based applications, which eliminates dev-ops silos and sprawl.
- Consistent operations and infrastructure: Provide edge, private and public cloud workload deployment options for a true hybrid cloud solution that maintains the flexibility of networking and topology.
- Automated end-to-end lifecycle management: Minimize SQL Server workload impact and downtime during the necessary patching and upgrading of the full private cloud stack using automated and self-managed services within the workload domain.
- Intrinsic Security at every level: Ensure the unified security and networking policies across organization with vSphere, NSX, and vSAN technologies such as vSphere vMotion® encryption, micro-segmentation, and data-at-rest storage encryption. VxRail has security built in at every level of the integrated technology stack.
- Simple path to hybrid cloud: Connect private and public cloud seamlessly and empower SQL Server compatibility of heterogeneous and distributed dataset with features such as scalable Big Data Cluster and data virtualization with PolyBase.
Key Results
This reference architecture is a showcase of VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail for operating and managing both Microsoft SQL Server 2019 VM-based and container-based database workloads in a fully integrated SDDC environment. Key results can be summarized as the following:
- VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail simplifies and accelerates the necessary virtualized and Kubernetes infrastructure deployment desired for traditional and modernized SQL Server workloads with automated workflow containing all the necessary sub tasks.
- VxRail provides linear scalability and predictable performance capability for SQL Server OLTP workloads in Windows virtual machines and SQL Server OLAP workloads in a container.
- A SQL Server workload domain consisting of four VxRail P570F nodes is capable of servicing up to 9,528 TPC-E like transaction per second with 21 milliseconds (ms) transactional response time for SQL Server virtual machines, together with 3.12GB/s TPC-H like bandwidth for SQL Server containers in VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid™. The aggregated peak vSAN throughput is over 190K in IOPS or 5.39GB/s in bandwidth with sub-millisecond backend latency.
- Tanzu Kubernetes Grid provides high availability and business continuity for containerized SQL Server workloads running on upstream compatible Kubernetes cluster, which can help tolerate various hardware and Kubernetes infrastructure level failure and outage.
- VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail is the ideal infrastructure to service both traditional VM-based and container-based SQL Server workloads on VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu platform, which enables consistent user experience and unified namespace management for virtual machines and containers encapsulated in vSphere Pod Service and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid.
Note: The performance results in this solution are tested based on the HCI platform of VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail, which also applies to general VMware vSAN with the similar hardware and software configurations. The test result is not for the maximum performance but only for the reference architecture validation purpose.
Audience
This solution is intended for IT administrators, cloud-native/Kubernetes developers, SQL Server DBAs, and storage experts who are involved in the early phases of planning, designing, and deploying of virtualized SQL Server workloads on VMware Cloud Foundation and Dell EMC VxRail. It is assumed that the reader is familiar with the concepts and operations of Microsoft SQL Server, VMware Cloud Foundation related components, and Dell EMC VxRail.
Technology Overview
Solution technology components are listed below:
- VMware Cloud Foundation
- VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu
- VMware vSphere
- VMware vSAN
- VMware NSX Data Center
- Dell EMC VxRail Hyperconverged Integrated System
- VxRail HCI System Software
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019
VMware Cloud Foundation
VMware Cloud Foundation is an integrated software stack that combines compute virtualization (VMware vSphere), storage virtualization (VMware vSAN), network virtualization (VMware NSX), and cloud management and monitoring (VMware vRealize Suite) into a single platform that can be deployed on-premises as a private cloud or run as a service within a public cloud. This documentation focuses on the private cloud use case. VMware Cloud Foundation bridges the traditional administrative silos in data centers, merging compute, storage, network provisioning, and cloud management to facilitate end-to-end support for application deployment.
VMware Cloud Foundation with VMware Tanzu
VMware Cloud Foundation with VMware Tanzu is a hybrid cloud platform that automates infrastructure deployment and lifecycle management of complex Kubernetes clusters alongside mission critical enterprise applications, including an embedded Kubernetes runtime environment that accelerates the development of modern applications.
VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu automates full-stack deployment and operation of Kubernetes clusters through the integration with VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid. This helps to eliminate manual steps for configuring host, creating logical relationships, managing hypervisors for faster deployment of applications at scale. VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu provides a comprehensive hybrid cloud platform that bridges the gap between app developers and IT administrators. VMware Cloud Foundation can be deployed on-premises on a broad range of vSAN ReadyNode™ servers, on engineered systems like Dell EMC VxRail, or consumed as a service in the public cloud from VMware Cloud on AWS, Azure VMware Solution, Google Cloud VMware Engine and select VMware Cloud™ Provider.
VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu is a major architectural upgrade to the industry’s most advanced hybrid cloud platform. The most exciting feature added to the VMware Cloud Foundation architecture is the integration of Kubernetes directly into the vSphere Hypervisor, which delivers an entirely new set of VMware Cloud Foundation Services, a new Kubernetes and RESTful API surface that empowers developers to have self-service access to Kubernetes clusters, vSphere Pods, virtual machines, persistent volumes, stateful services, networking resources, etc. These services include VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid plus infrastructure and automation services that provide the basis for the cloud infrastructure and container ecosystems to boost developer productivity. VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu represents a major advancement in cloud-native compute, storage, networking, and management to seamlessly support containers and VMs all within the same automated hybrid cloud infrastructure.
VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere is the next-generation infrastructure for next-generation applications, which provides a powerful, flexible, and secure foundation for business agility that accelerates the digital transformation to cloud computing and promotes success in the digital economy. VMware vSphere embeds containers and Kubernetes into vSphere, unifying them with virtual machines as first-class citizens. This enables all vSphere administrators to become Kubernetes administrators and easily deliver new services to their developers. VMware vSphere addresses key challenges faced by the IT admins in areas of lifecycle management, security, and performance and resiliency needed by business-critical applications, AI/ML applications and latency sensitive applications. With VMware vSphere, customers can run, manage, connect, and secure both traditional and cloud-native applications in a common operating environment, across clouds and devices.
VMware vSAN
VMware vSAN is the industry-leading software powering VMware’s software defined storage and HCI solution. vSAN helps customers evolve their data center without risk, control IT costs, and scale to tomorrow’s business needs. vSAN, native to the market-leading hypervisor, delivers flash-optimized, secure storage for all of your critical vSphere workloads, and is built on industry-standard x86 servers and components that help lower TCO in comparison to traditional storage. It delivers the agility to scale IT easily and offers the industry’s first native HCI encryption.
vSAN simplifies Day 1 and Day 2 operations, and customers can quickly deploy and extend cloud infrastructure and minimize maintenance disruptions. vSAN helps modernize hyperconverged infrastructure by providing administrators a unified storage control plane for both block and file protocols and provides significant enhancements that make it a great solution for traditional virtual machines as well cloud-native applications. vSAN helps reduce the complexity of monitoring and maintaining infrastructure and enables administrators to rapidly provision a file share in a single workflow for Kubernetes-orchestrated cloud native applications.
VMware NSX Data Center
VMware NSX Data Center is the network virtualization and security platform that enables the virtual cloud network, a software-defined approach to networking that extends across data centers, clouds, and application frameworks. With NSX Data Center, networking and security are brought closer to the application wherever it’s running, from virtual machines to containers to bare metal. Like the operational model of VMs, networks can be provisioned and managed independently of the underlying hardware. NSX Data Center reproduces the entire network model in software, enabling any network topology—from simple to complex multitier networks—to be created and provisioned in seconds. Users can create multiple virtual networks with diverse requirements, leveraging a combination of the services offered via NSX or from a broad ecosystem of third-party integrations ranging from next-generation firewalls to performance management solutions to build inherently more agile and secure environments. These services can then be extended to a variety of endpoints within and across clouds.
Dell EMC VxRail Hyperconverged Integrated System
The only fully integrated, pre-configured, and pre-tested VMware hyperconverged integrated system optimized for VMware vSAN and VMware Cloud Foundation, VxRail transforms HCI networking and simplifies VMware cloud adoption while meeting any HCI use case - including support for many of the most demanding workloads and applications. Powered by Dell EMC PowerEdge server platforms and VxRail HCI System Software, VxRail features next-generation technology to future proof your infrastructure and enables deep integration across the VMware ecosystem. Advanced VMware hybrid cloud integration and automation simplifies the deployment of a secure VxRail cloud infrastructure.
VxRail HCI System Software
VxRail HCI system software is integrated software that delivers a seamless and automated operational experience, offering 100% native integration between VxRail Manager and vCenter. Intelligent lifecycle management automates non-disruptive upgrades, patching, and node addition or retirement while keeping VxRail infrastructure in a continuously validated state to ensure that workloads are always available. The HCI System Software includes SaaS multi-cluster management and orchestration for centralized data collection and analytics that uses machine learning and AI to help customers keep their HCI stack operating at peak performance and ready for future workloads. IT teams can benefit from actionable insights to optimize infrastructure performance, improve serviceability, and foster operational freedom.
.png)
Figure 1. VxRail Manager and SDDC Manager Integration
Microsoft SQL Server 2019
Microsoft SQL Server 2019 is the new data platform to solve challenges from the modern data professional and host data on the platform of choice with the compatibility of Windows, Linux, Docker Containers, or orchestrated by Kubernetes. It introduces Big Data Cluster that combines the power of SQL Server, Hadoop, Apache Spark, and Kubernetes to provide end-to-end and machine learning platform. SQL Server 2019 simplifies the deployment of containers and Kubernetes both on premise and on the cloud with elasticity and portability. It also enhances mission-critical workloads security with Always Encrypted with Secure Enclaves and the maximum database availability with the accelerated recovery. In this solution, we adopted SQL Server 2019 on Red Hat containers, which demonstrated the deployment agility, management reliability, data security, and performance improvements of SQL Server running on Kubernetes platform.
Solution Configuration
This section introduces the resources and configurations:
- Architecture diagram
- Hardware resources
- Software resources
- Network configuration
- Virtual machine configuration
Architecture Diagram
Figure 1 shows the reference architecture of modernizing Microsoft SQL Server 2019 on VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail. We created a 4-node VxRail P570F cluster for VMware Cloud Foundation management cluster, running multiple management virtual machines and appliances including:
• A management vCenter Server appliance with Platform Service Controllers embedded
• Three NSX-T Manager appliances for management cluster
• A VxRail Manager
• A workload domain vCenter Server appliance
• Three NSX-T Manager appliances for SQL Server workload domain
For the SQL Server workload domain cluster, we created another 4-node VxRail P570F cluster. We deployed four SQL Server 2019 on Windows virtual machines to simulate the production workloads using TPC-E like OLTP benchmark. With the help of VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu, we modernized SQL Server in containers on the Kubernetes infrastructure with the capability for container namespace management and image registry service. The database administrator may determine the Kubernetes platform for running the SQL Server containers:
• Run SQL Server container natively in vSphere Pod to gain consistent management and user experience as virtual machine.
• Run SQL Server container in Tanzu Kubernetes Cluster to gain upstream compatibility, automated self-provisioning, high availability protection of Kubernetes infrastructure.
In this solution, we used Tanzu Kubernetes Gird Service to provision a Tanzu Kubernetes cluster of 3 control plane nodes and 4 worker nodes and deployed totally 4 SQL Server Red Hat containers on each of them. The containerized SQL Server workload was simulated by TPC-H like OLAP workload as non-production environment. A Harbor image registry was configured to provide local image service for both containers running in vSphere Pod and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid.
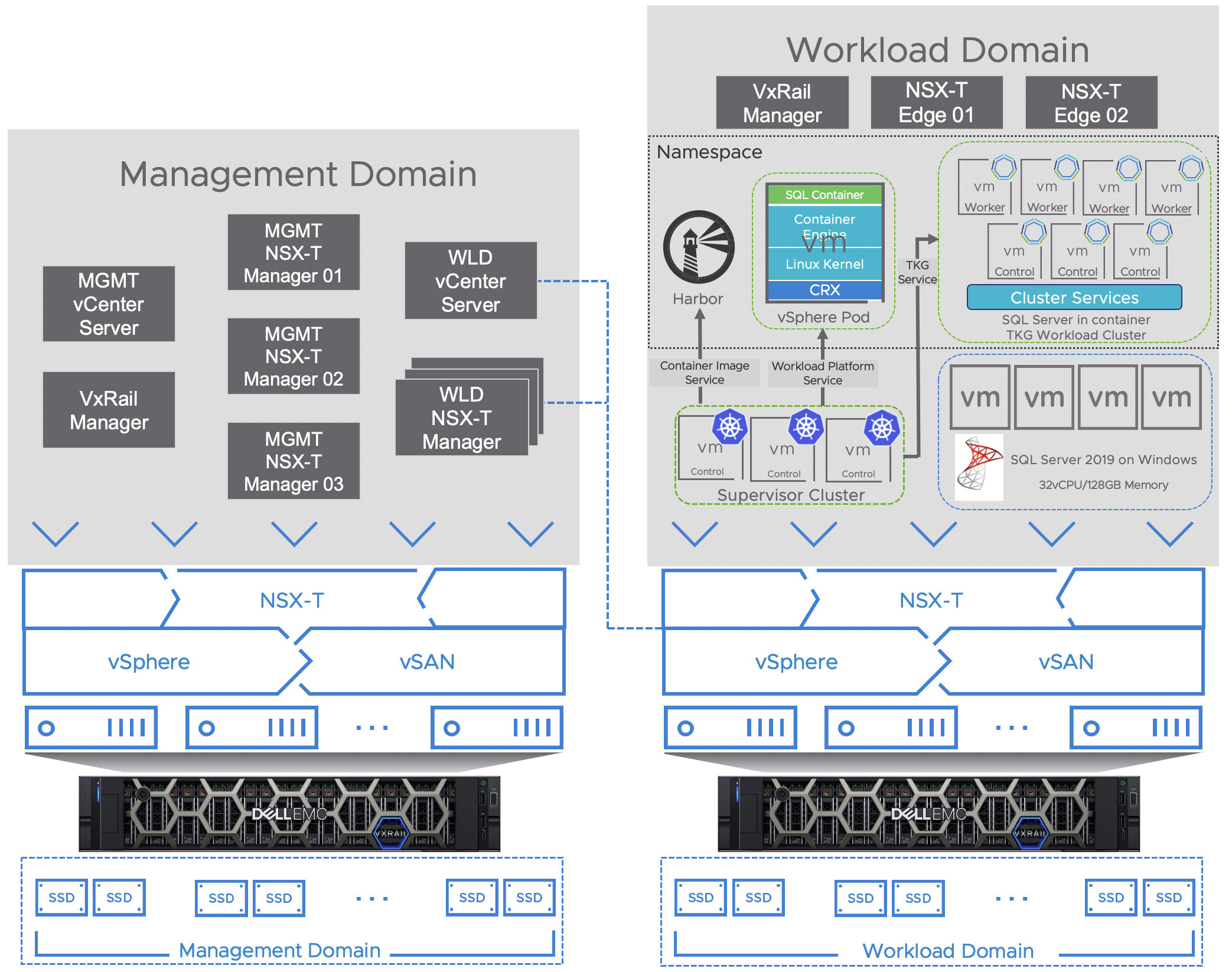
Figure 1. Architectural Diagram
Hardware Resources
Table 1 shows the hardware configuration used in this solution.
Table 1. Hardware Configuration
|
PROPERTY |
SPECIFICATION |
|
Server model name |
8 x VxRail P570F |
|
CPU |
2 x Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8180M CPU @ 2.50GHz, 28 core each |
|
RAM |
512GB |
|
Network adapter |
2 x Broadcom BCM57414 NetXtreme-E 10Gb/25Gb RDMA Ethernet Controller |
|
Storage adapter |
1 x Dell HBA330 Adapter |
|
Disks |
Cache - 2 x 800GB Write Intensive SAS SSDs Capacity - 8 x 3.84TB Read Intensive SAS SSDs |
Software Resources
Table 2 shows the software resources used in this solution.
Table 2. Software Resources
|
Software |
Version |
Purpose |
|
VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail |
4.0 |
A unified SDDC platform on Dell EMC VxRail that brings together VMware ESXi, vSAN, NSX, and optionally, vRealize Suite components, into a natively integrated stack to deliver enterprise-ready cloud infrastructure for the private and public cloud. See BOM of VMware Cloud Foundation on VxRail for details. |
|
Dell EMC VxRail |
7.0.000 |
Turnkey Hyperconverged Infrastructure for hybrid cloud |
|
Windows Server 2019 |
Standard |
Operating system |
|
Microsoft SQL Server 2019 on Windows |
SQL Server on Windows platform Enterprise edition 2019 CU5 |
Microsoft SQL Server database server platform on Windows |
|
Microsoft SQL Server 2019 container |
SQL Server on Red Hat container Enterprise edition 2019-CU5-rhel-8 |
Official image for Microsoft SQL Server on Red Hat container |
|
SQL Server management studio |
18.5.1 |
Integrated environment for managing any SQL infrastructure |
|
Benchmark Factory for Databases |
8.1 |
SQL Server OLTP workload generation tool |
Network Configuration
Figure 2 shows the VMware vSphere Distributed Switch™ network configuration for the SQL Server workload domain of the VMware Cloud Foundation on VxRail. To enable workload management for containerized SQL Server workload, an NSX-T edge cluster is required to deploy, and the BGP peering and route distribution of the upstream network is required to configure. For more details, refer to VMware Cloud Foundation 4.0 on VxRail Planning and Preparation Guide.

Figure 2. Virtual Distributed Switch Configuration
Virtual Machine Configuration
Table 3 shows the virtual machine configuration of the VMware Cloud Foundation management domain in this solution.
Table 3. Management Domain Virtual Machine Configuration
|
VM Role |
vCPU |
Memory (GB) |
VM Count |
|
Management Domain VxRail Manager |
2 |
8 |
1 |
|
Management Domain vCenter Server |
4 |
19 |
1 |
|
SDDC Manager |
4 |
16 |
1 |
|
Management Domain NSX Manager |
6 |
24 |
3 |
|
SQL Server Workload Domain vCenter Server |
12 |
48 |
3 |
|
SQL Server Workload Domain NSX Manager |
6 |
24 |
3 |
|
Cloud Builder |
4 |
4 |
1 |
Table 4 shows the virtual machine configuration of the VMware Cloud Foundation SQL Server workload domain in this solution. We enabled the vSphere workload management with 3 supervisor cluster control VMs for cloud native workload namespace management and pod service. And we also created a Tanzu Kubernetes cluster with 3 control plane nodes and 4 worker nodes for modernized SQL Server container workload.
Table 4. SQL Server Workload Domain Virtual Machine Configuration
|
VM Role |
vCPU |
Memory (GB) |
VM Count |
Disk Layout |
|
SQL Server on Windows |
32 |
128 |
4 |
OS: 1 x 100 GB Data: 4 x 250 GB TempDB and Log disk: 1 x 200 GB |
|
NSX-T edge appliance |
8 |
32 |
2 |
OS: 200GB |
|
Supervisor cluster control plane VM |
16 |
32 |
3 |
OS: 22GB |
|
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid control plane VM |
4 |
32 |
3 |
OS: 16GB |
|
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid worker VM |
4 |
32 |
4 |
OS: 16GB |
Solution Validation
Test Overview
This solution demonstrates deploying, running, and managing both VM based and containerized SQL Server 2019 workloads on VMware Cloud Foundation platform powered by Dell EMC VxRail. We simulated the production OLTP workloads with TPC-E like benchmark running on traditional virtual machines, and the OLAP workloads for test/dev, database analysis and repurposing with TPC-H like benchmark running on top of the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Cluster.
We also performed various failure tests to demonstrate the workload consistency of the containerized SQL Server running on Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Cluster.
Test Tools
We used the following monitoring tools and benchmark tools in the solution testing:
- Monitoring tools
vSAN Performance Service
vSAN Performance Service is used to monitor the performance of the vSAN environment, using the vSphere client. The performance service collects and analyzes performance statistics and displays the data in a graphical format. You can use the performance charts to manage your workload and determine the root cause of problems.
vSAN Health Check
vSAN Health Check delivers a simplified troubleshooting and monitoring experience of all things related to vSAN. Through the vSphere client, it offers multiple health checks specifically for vSAN, including cluster, hardware compatibility, data, limits, physical disks. It is used to check the vSAN health before the mixed-workload environment deployment.
Windows Performance Monitor
Windows Performance Monitor is a Windows tool that enables users to capture statistics about CPU, memory, and disk utilization from operating system levels. It also provides counters for monitoring SQL Server and Exchange performance and status.
- Database generation tools
Benchmark Factory for Databases
Benchmark Factory for Databases (BMF) is a database workload generation tool that can conduct industry-standard benchmark testing and scalability testing. With Benchmark Factory for databases, you can make changes to your database environment and mitigate the risks of planned database changes. We used this tool to generate SQL Server database TPC-E like OLTP workload.
- Kubernetes CLI tools
Kubectl + vSphere plugin
The Kubernetes CLI Tools download package includes two executables: the standard open source kubectl and the vSphere Plugin for kubectl. The kubectl CLI has a pluggable architecture. The vSphere Plugin for kubectl extends the commands available to kubectl so that you connect to the Supervisor Cluster and to the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid clusters using vCenter Single Sign-On credentials.
Deploy SQL Server 2019 on VMware Cloud Foundation
We deployed four VxRail nodes for the management cluster and another four VxRail nodes for the workload domain dedicated for SQL Server. It is highly recommended to follow the steps described in VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail Admin Guide. For more details and instructions, contact VMware and Dell EMC Customer Services or your sales representative.
To modernize SQL Server 2019 with cloud native workloads, we enabled workload management for VMware Cloud Foundation and deployed a SQL Server container with Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service. Figure 3 shows the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid cluster with 3 control plane VMs and 4 workers VMs of guaranteed-xlarge virtual machine class deployed for solution validation. Refer to Virtual Machine Class Types for Tanzu Kubernetes Clusters and Example YAML Files for Provisioning Tanzu Kubernetes Clusters for more details.

Figure 3. Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Cluster
Workload Consolidation Test
The workload consolidation test is designed to validate the performance scalability and consistency of running both VM based and containerized SQL Server workloads together in a database workload domain of VMware Cloud Foundation.
Table 5 describes the VM-based and container-based SQL Server configuration in this test scenario. The container that hosts the SQL Server instance is described as a Kubernetes deployment object, which creates the replica set, and the replica set will finally create the SQL Pod in Kubernetes. A 2TB persistent volume was created and attached to the SQL Pod as storage for SQL in container binary and test database. We applied a storage policy with stripe width set to 4 to help distribute container database across cluster and help improve OLAP performance. For more details about creating SQL Server containers on Kubernetes, visit Deploy a SQL Server Container in Kubernetes with Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS).
Table 5. VM-based and Container-based SQL Server Configuration
|
SQL Server platform |
vCPU |
Memory |
Storage Policy |
Database size |
Workload Profile |
|
Windows Server 2019 virtual machine |
32 |
128GB (120GB allocated to SQL Server instance) |
vSAN default storage policy |
600 GB |
Industry brokerage system, TPC-E like OLTP workload, 90/10 read/write ratio, 8KB majority block size. Simulated 50 virtual users/connections. |
|
Red Hat container |
4 |
32GB (25.6GB allocated to SQL Server instance) |
SQL Server container storage policy with “Number of disk stripes per object” = 4 |
600 GB |
Decision support system, TPC-H like OLAP workload, sequential read intensive, block size is multiple of 8KB, can be up to 512KB. Simulated 22 T-SQL analysis queries. |
Figure 4 and Figure 5 showed the consolidated OLTP and OLAP SQL Server workloads results running on top of VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail. The overall achieved performance was 9,528 aggregated TPS in VM-based SQL Server OLTP workload and together with 3.12 GB/s aggregated bandwidth in container-based SQL Server OLAP workloads.
With one SQL VM plus one SQL Pod test as a baseline, both the OLTP and OLAP performance scaled linearly as we added more SQL VMs and Pods. The transactional response time of OLTP workload was maintained at 21 milliseconds and the peak vSAN bandwidth achieved was around 5.39 GB/s with sub-millisecond backend storage latency. The test result demonstrated that VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail could not only service the traditional SQL Server workload with highly scalable and stable performance, but also modernized the containerized SQL Server workload and offloaded OLAP jobs to VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu platform for faster test/dev iteration, various database repurposing, and analysis capability.


Figure 4. Consolidated Workload Result – TPC-E like Workload Figure 5. Consolidated Workload Result – TPC-H like Workload
SQL Server Failure Test
This test is designed to demonstrate how Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service provided by VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu can tolerate different failures situations and maintain business continuity of the containerized SQL Server workloads.
The failure test scenarios are designed as follows:
- SQL Pod failure: we simulated this type of failure by force killing a SQL Pod with the “kubectl delete pod” command.
- Tanzu Kubernetes Grid worker node failure: we simulated this type of failure by force powering off one of the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid worker node with the “kill vm process” command.
- VxRail maintenance mode: we simulated this type of failure by entering maintenance mode in vCenter UI of VxRail node that the SQL Pod resides.
- VxRail planned/unplanned shutdown/poweroff: we simulated these types of failures on VxRail by either normal shutting down process or force powering off using the iDRAC that the SQL Pod resides.
We simulated the TPC-H like workload against the test SQL Server Pod and monitored the performance during each of the failure test. For simplicity, we selected one out of the 22 TPC-H like queries and ran the query repeatedly for one hour. The interval of the performance counter was set to 20 seconds. We also configured the reconnection mechanism on the Benchmark Factory for database if the benchmark tool detected a temporary failure of the SQL Server container.
Figure 6 showed the SQL Server Pod failure test result. Because the SQL query is executed repeatedly, you will find a similar bandwidth pattern for each query execution round. During the fourth query execution cycle, we issued the Pod deletion command, and it was eliminated immediately. However, as the container hosting the SQL Server instance was described as a Kubernetes deployment object defined in the yaml file, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid cluster would help recreate the SQL Server Pod and attached the existing persistent volume that the SQL Server binary and database resided. The bandwidth dropped to zero during the Pod recreation process for less than a minute. After the new SQL Server Pod was up and running, the workload can resume to normal as usual.

Figure 6. Workload Behavior of SQL Server Pod Failure
In the second failure test, we forcibly powered off the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid worker node that the SQL Pod was running to simulate a worker node failure. By default, VMware vSphere High Availability will try to restart the worker node if there is a potential failure in the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid cluster. We issued the “kill vm process” command in the fourth cycle and observed the SQL Pod performance. After the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid node was forcibly powered off, the SQL workload dropped to zero immediately. We observed that vSphere High Availability restarted the VM within 40 seconds after the failure occurred. And the SQL Pod was being restarted on the same Tanzu Kubernetes Grid worker node within 6 minutes so that the container workload was back to normal.

Figure 7. Workload Behavior of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Worker Node Failure
In the third failure test as shown in Figure 8, during the third query cycle, we put one of the VxRail node where the SQL Server Pod resided into maintenance mode and observed the performance impact. After the host kicked entering the maintenance mode, the impacted Tanzu Kubernetes Grid worker node performed a live migration to another VxRail node; thus, no application downtime was observed during this type of failure test. We observed a certain performance drop after the vMotion activity, and the performance would gradually return to a normal state.

Figure 8. Workload Behavior of Host Maintenance Mode
In the last failure test as shown in Figure 9, we performed an unplanned host poweroff through VxRail iDRAC to simulate a power outage. You can see the impacted Tanzu Kubernetes Grid worker node that the SQL Server Pod ran on would be restarted by vSphere High Availability on another VxRail node. After the worker node was powered on and resumed the service, the SQL Server Pod would be restarted on this worker node and attached the corresponding persistent volume to start the service. The SQL Server container workload was observed to continue within 5 minutes. This test result also applies to the planned system shutdown of a VxRail node.

Figure 9. Workload Behavior of VxRail Planned/Unplanned Shutdown/Poweroff
Best Practices
In this solution, we validated a SQL Server on Windows virtual machine with TPC-E like OLTP workload and a SQL Server container on Tanzu Kubernetes Grid with TPC-H like OLAP workload.
The following recommendations provide the best practices and sizing guidance to run SQL Server on VMware Cloud Foundation on VxRail.
- Modernized workload platform consideration:
- Consider running the SQL Server containerized workloads natively in VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu Supervisor cluster to gain consistent management of Kubernetes namespaces and unified operational experience just like a virtual machine.
- Consider running SQL Server containerized workloads with Tanzu Kubernetes Grid for upstream compatible Kubernetes environment and highly automated Kubernetes infrastructure of management simplicity.
- Compute consideration:
- Enable vSphere High Availability and vSphere DRS for SQL Server in container workloads that reside in vSphere Pod or Tanzu Kubernetes Grid clusters for optimized and automated pooling and scheduling.
- Configure Anti-affinity rules whereas multiple SQL Server instances running in separate virtual machines. For large SQL Server instance, it is recommended to configure VM override rules to avoid unnecessary vMotion activity.
- Configure enough CPU/memory resources for SQL Server production workloads in a virtual machine. SQL Server in a container by default is configured with 80 percent memory of the available size.
- Network consideration:
- Separate the physical network using different network range and VLAN ID for management, vSphere vMotion, vSAN, VM network, and overlay network.
- For NSX-T Data Center design best practices for workload domain, see the VMware® NSX-T Reference Design Guide.
- Storage consideration:
- For VM-based SQL Server OLTP workloads, follow the generic best practices for Architecting Microsoft SQL Server on VMware vSphere.
- For container-based SQL Server OLAP workloads, consider increasing the “Number of disk stripes per object” for the storage policy associated with the persistent volume claim to improve object spreading and performance.
- Leave the default value of failure to tolerate (FTT) to 1 for the storage policy of persistent volume used by the containerized SQL Server running on Tanzu Kubernetes Grid.
- Create a dedicated vSAN storage policy for management and isolation purposes of VM-based and container-based SQL Server workloads.
Conclusion
VMware Cloud Foundation on Dell EMC VxRail is the ideal hybrid cloud platform for traditional mission-critical SQL Server workloads in virtual machines and modernized SQL Server workloads in containers. VMware Cloud Foundation delivers the enterprise-class resiliency, QoS, security and access control for both SQL Server VMs and containers. As enterprises adopt more and more modern application workloads, VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu provides Kubernetes namespace integration and storage policy-based management to enable administrators who used to manage thousands of VMs can now manage cloud-native applications on Kubernetes in the same manner. At the same time, database administrators can migrate SQL Server databases to container with cloud resources such as Kubernetes cluster, persistent volumes, and networks on the same platform that VMs used to reside on.
In this solution, we validated the performance capability and infrastructure resiliency of both SQL Server OLTP workloads in virtual machines and OLAP workloads in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid clusters on top of VMware Cloud Foundation with Tanzu. The result proves the consolidation and collaboration of traditional and modernized SQL Server workloads on the same platform with rapid deployment of virtualization and Kubernetes infrastructure, unified management of virtual machines and containers, automated lifecycle management of hardware and software stack, and intrinsic security at every layer of compute, network, and storage.
Reference
About the Author
Mark Xu, Solutions Architect in the Solutions Architecture team of the Cloud Platform Business Unit, wrote the original version of this paper.
The following reviewers also contributed to the paper contents:
- William Leslie, Sr. Manager of VxRail Technical Marketing in Dell EMC
- Vic Dery, Sr. Principal Engineer of VxRail Technical Marketing in Dell EMC
- Jason Marques, Sr. Principal Engineer of VxRail Technical Marketing in Dell EMC
- George OTooleIii, Sr. Advisor of Product Marketing in Dell EMC
- Linwood Zoller, Sr. Principal Engineer, Kubernetes and Cloud-Native Apps on VxRail
- Kyle Gleed, Staff Technical Marketing Architect of the Cloud Platform Business Unit in VMware
