What is the SDDC Manager? And why do I need another appliance?
Introduction
The SDDC manager is more than just another appliance, In this blog I'll dive into the details of what the SDDC manager does and how it delivers a private cloud with VMware Cloud Foundation.
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) is an enterprise class private cloud infrastructure platform for your on-premises datacenter. A key to delivering this cloud infrastructure capability is the automation of the cloud platform. SDDC Manager is the automation engine that orchestrates all the software defined data center infrastructure components. Looking deeper into this private cloud platform, we will see how the SDDC manager and all the VCF components come together and deliver, Automation, Architecture, Scale, Lifecycle, Security and more.

Automation
The SDDC manager is created on day-zero with the installation of VMware Cloud Foundation using the Cloud Builder VM. The Cloud Builder automates the installation and configuration of the entire SDDC infrastructure software stack. Included with VMware Cloud Foundation is, vSphere, vSAN, NSX, and Aria Suite. During this installation the SDDC Manager appliance is instantiated and together, these products bring a full private cloud infrastructure suite. Below is a VCF installation report, As you can see from this report, just doing the initial bring up process is over 150 steps that are completed with VCF automation.
Click here to download a VCF Bringup deployment Report
After the initial installation of VCF, the SDDC Manager automates the scale out modular deployment of the core VMware Cloud Foundation stack, including VMware vSphere (compute virtualization), VMware vSAN (storage virtualization), VMware NSX (network virtualization), along with deep integration of the Aria Suite (cloud management and monitoring). This automation reduces the complexity and time required to scale out the cloud infrastructure platform.
Most vSphere admins have manually deployed infrastructure software before and know that gathering all the required inputs and keying them in can take weeks or even months depending on the size and scale of the environment. Each step is an opportunity for human error. Leveraging automation from a self-service catalog is not only faster, but eliminates human error and creates a consistent repeatable infrastructure. This consistency leads to increased time to value as you don't need to retrain staff on different software tools or have staff with multiple skillsets. The SDDC manager simplifies infrastructure, delivering digital transformation through a automated self service catalog to continue to scale and manage the infrastructure.

Scalable Architecture
The SDDC Manager uses automation to deploy a modular architecture, allowing organizations to deploy and scale individual components based on their specific requirements. This modular approach enables organizations to choose the cloud architecture that is tailored to different use cases and application workloads.
Let's dive into the different architectural choices of VMware Cloud Foundation. Note: As read below, keep in mind, this architecture is all built into the SDDC Manager automation.
Workload Domain
The Workload Domain might be a new term for a vSphere administrator. The Workload Domain is a key modular building block for VMware Cloud Foundation infrastructure.
A Workload Domain is what you already know as a vCenter with a ESXi compute cluster. But when its deployed with VCF a Workload Domain is deployed with automation and that automation follows a prescribed architecture.

That architecture includes, taking a group of ESXi hosts and deploying them with their own vCenter Server, installing and configuring Software Defined Networking (SDN), and provisioning storage.
When this is all deployed, from here on out, this Workload Domain is now managed by the SDDC Manager. Think of the SDDC Manager as central command and control for the infrastructure components. You can create, expand, contract, delete and lifecycle manage the Workload Domain infrastructure all with automation. When you think about comparing this to public cloud infrastructure, this is the same thing, you just now have that cloud level of control in your private datacenter.
Types of Workload Domains
Workload Domains come in two types.
Upon initial creation of VCF, we create the first type, the Management Workload Domain.

This is where almost all the Management VMs are placed, Management VMs including vCenter server, NSX managers, Aria appliances, and any other 3rd party management and operations applications you might have to operate your private cloud would be deployed here in the management workload domain. Now, depending on the size of your infrastructure, this single Management Domain is possibly all you need to run your business applications. As you can also deploy and operate business applications in the Management Workload Domain. This is fully supported.
But for larger enterprises we offer a second type of Workload Domain.
A Virtual Infrastructure (VI) Workload Domain, is the second type, and this Workload Domain is made purpose built just for running your business applications.

This workload separation creates an architecture that separates your management applications from your business applications. Businesses love this architecture! With this approach the management applications are not on the same host as the business applications, preventing any noisy neighbor situations. These are the two core Workload Domain Architectures for VMware Cloud Foundation.
Diving deeper into this architecture, let's look at what's possible with VCF. And get an understanding of when you would leverage these Workload Domains for different business needs and see how they scale.
Multiple Workload domains
Speaking of scale, very large enterprises might need more workload separation or additional boundaries. To account for this, we can also provide multiple Workload Domains.
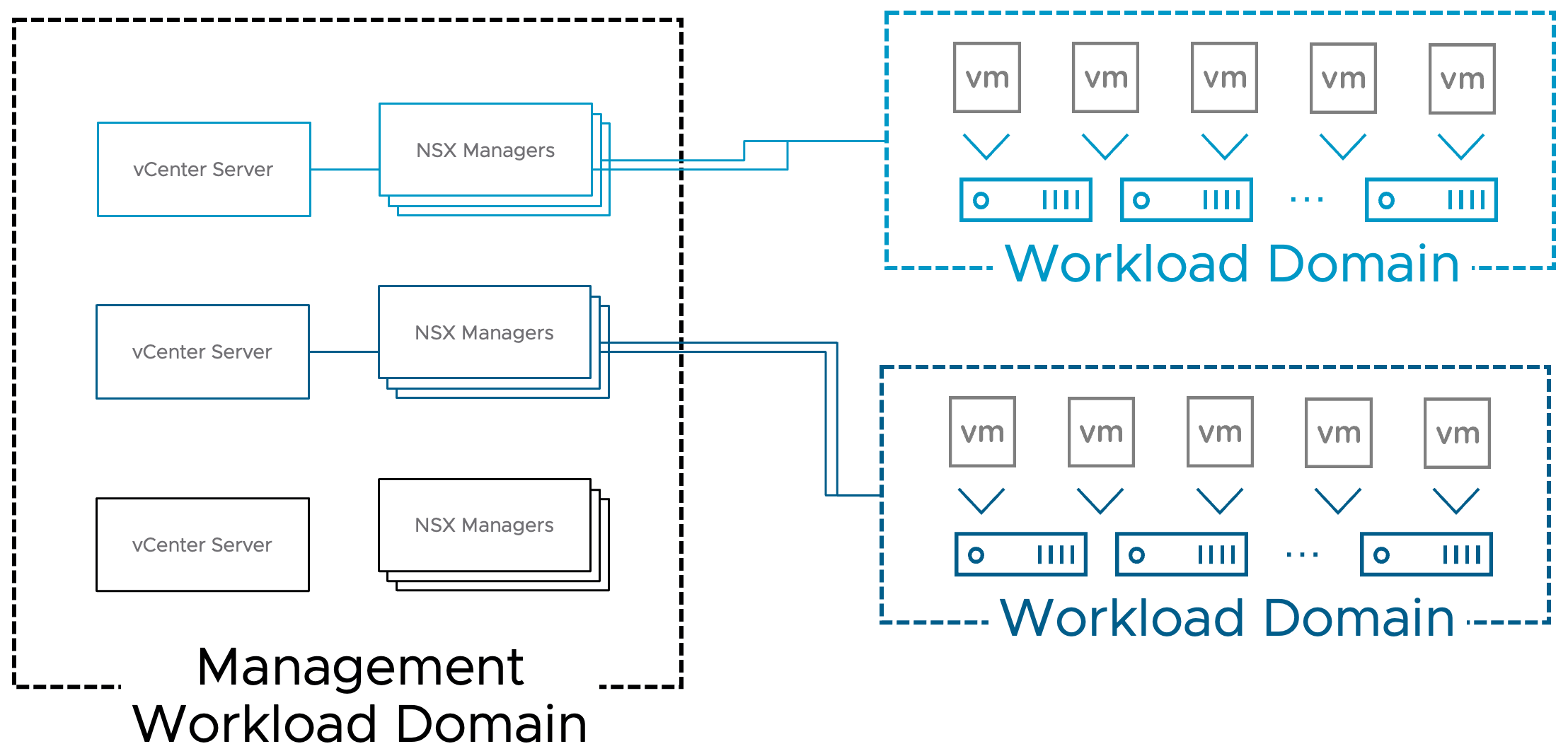
As you can see from the diagram above, each Workload Domain comes with its own vCenter, NSX software defined network management plane, and storage is also separated.
You might be thinking, why is this necessary? Here are a few ways we see this used. Workload Domains create workload separation by creating boundaries around the management components as well as the hosts, storage, and networks. You can give an entire Workload Domain to the Windows admins, let them have their own vCenter, NSX, Storage and ESXi hosts. Give another Workload Domain for Linux admins and let them have their own vCenter, NSX management, and Storage.

One of the best use cases for this is, Lifecycle management. Each of these Workload Domains can be patched and upgraded independently of each other. The Windows Admins, can follow their scheduled for patching on patch Tuesday, while the Linux team can do all their patches and upgrades on their own schedule, completely independent of each other.
There are many other reasons to create these vCenter boundaries as well. You could create a Workload Domain for desktop admins to operate virtual desktops, create a Workload Domain for DMZ applications, to help maintain a highly secure environment for applications that are accessed over the internet. Or act as a cloud service provider for your different business units.
Each use case maintains workload separation for complete flexibility.
Remote Workload Domain Clusters
Workload Domains can also deploy remote clusters, to remote sites.

Here we have a two node Remote Cluster site leveraging some 3rd party storage. Then another remote cluster site using three or more hosts and leveraging vSAN as the backend storage.
Notice how the Management plain remains in the Management workload Domain site. Remote sites have some latency requirements and a requirement for redundant site links. See the latest documentation for the required metrics for Remote Clusters.
As we have seen so far, VMware Cloud Foundation can be deployed, with several architectural choices to meet various business needs.
Network Management Plane
VCF also has flexibility around how we deploy and use the NSX management plane. Some of our customers, like to keep things simple and leverage a single network management plane for their SDDC.

As you can see from the diagram above, each Workload Domain comes with its own vCenter server instance. Workload Domains may have a dedicated NSX software defined network management plane, or they can share a common NSX management plane (more on this below). Inside each Workload Domain vSphere clusters are deployed with dedicated storage.
This gives you the flexibility to choose how you want to architect the network management plane for your cloud environments.
Isolated Single Sign On
Next, we have several options for organization that want to operate as a Cloud Service Provider. To provide a cloud service in your private datacenter, you also need to provide independent Single Sign On (SSO) authentication for Workload Domains. By default, each Workload Domain is using the same SSO domain. But VCF has multiple SSO design options to meet various business requirements.

With VMware Cloud Foundation you have a choice for SSO domain Isolation. When you create a Workload Domain, to you can choose to join the existing Management SSO Domain or create a new Isolated Workload Domain. Shown above here, we have them mixed with shared and Isolated SSO domains, and we also support full Isolation.
To operate more like a Cloud Service Provider (CSP), complete SSO domain Isolation for each Workload Domain is required. As shown below Workload Domains would be completely isolated from an SSO domain perspective, yet, the CSP would be able to maintain control of all scale and lifecycle operations for the infrastructure Workload Domains.

vSAN Stretched Clusters
Another deployment option can be used to leverage two sites and provides active-active high availability. Cloud Foundation also supports vSAN stretched cluster deployments between two sites. These two sites need to be within close proximity to support vSAN Replication latency requirements for this high availability solution.

Stretched vSAN clusters can be useful for performing planned maintenance on a site without any downtime. Applications can be migrated back after the maintenance is completed.
This highly available architecture prepares your business for disaster avoidance by preventing service outages in the event of a site link failure or other disasters.
Multi-Cluster Workload Domains
Cloud Foundation scales up with ease as well, we also can create multiple clusters inside individual Workload Domains. Scaling up clusters is all done with automation just like any other cloud infrastructure.

As we show in this example, with three clusters deployed within one Workload Domain. Note that three isn't a limit, just an example, to see the latest VCF documentation for scale up maximums.
As I mentioned earlier, all of these architectures are deployed by SDDC Manager. The SDDC manager allows for the dynamic addition or removal of cloud infrastructure resources, helping organizations adapt to changing workload demands without manual intervention. As described here, VCF can scale by adding hosts, clusters, workload domains, and much more all with the powerful cloud automation of the SDDC manager.
Lifecycle Management
Moving beyond architecture and scale, SDDC Manager also provides unified lifecycle management for the core SDDC stack. It automates routine tasks such as patching, and upgrading, ensuring that the components are consistently maintained and up-to-date. This reduces the risk of errors associated with manual processes and helps maintain a healthy and secure infrastructure.
Patching a full SDDC infrastructure stack can be a daunting manual task. There are multiple interdependencies to validate and be aware of. You need to make sure each piece in the stack is patched or upgraded in the right order.

This is where the SDDC Manager really shines. The SDDC Manager takes care of all the interdependencies for you, orchestrating the patches the SDDC in a fully automated prescribed order of operations.

This automation eliminates human errors during maintenance windows, and over time our customers have told us that their business application owners see the increase in the stability the infrastructure compared to manual deployments. This is now allowing some of our customers to do upgrades during normal business hours. And they have seen drastic reductions in infrastructure outage calls.
Infrastructure as Code API
The APIs provided by the SDDC Manager allow for the automation of numerous tasks across storage, compute, and networking resources. This allows our customers to deploy and manage the environment with more efficiency, and as a result enjoy a faster time to market for their services.
Cloud Foundation is built with API automation in mind. Cloud Foundation has a comprehensive, standardized set of APIs that are important for customers who want to integrate their existing toolsets to automate infrastructure tasks in Cloud Foundation. This API support helps our customers to accelerate adoption of the SDDC by easing the integration of their VMware and 3rd party business systems into Cloud Foundation. Allowing our customers to protect their investments in their existing IT and business centric systems by programmatically integrating them to manage and provision SDDC infrastructure as code using a standardized set of APIs and giving them the power of cloud in their private data centers.

Cloud Foundation provides a series of infrastructure focused APIs. These APIs are used to perform tasks such as the addition or removal of hosts to the solution, adding or deleting clusters, creating workload domains, and many more.

Security
With multiple components to the SDDC, there is a lot to pay attention to when it comes to security. I'll cover a just a few of the security components that are specific to the SDDC Manager itself. But keep in mind that VCF also includes security throughout the entire platform including, vSAN data at rest encryption, vSAN data in flight encryption, optional NSX distributed firewalls, ESXi Lockdown mode along with complete guidance on DoD STIG for VCF.
More specific to the SDDC Manager though I'll focus on two security components. Password management and SSL Certificate automation.
Password management
The SDDC Manager provides centralized password management across the entire cloud infrastructure stack. This centralization simplifies the process of managing passwords for various components such as compute, storage, networking, and management services.

Automated workflows can handle tasks such as password rotation, synchronization, and distribution, improving efficiency and reducing administrative overhead. The SDDC Manager also integrates with identity management systems such as Active Directory, LDAP, or SAML, enabling organizations to centralize user authentication and access control. This integration ensures that password management is aligned with existing identity and access management processes and policies. Recent additions to VCF authentication include support for Okta as an external identity provider and Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) as an external identity provider, instead of using vCenter Single Sign-On.
In addition, the SDDC manager supports RBAC mechanisms for controlling access to password management functions based on user roles and responsibilities. This granular access control helps organizations enforce least privilege principles and minimize the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive password information. Audit trails and logging capabilities built into the SDDC manager for password management activities, allow organizations to track changes, monitor access, and demonstrate compliance with security policies and regulatory requirements. Passwords are all encrypted and securely stored using mechanisms to protect passwords from unauthorized access or disclosure.
SSL Certificate automation
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) Certificate management within VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) is fully automated by the SDDC manager. This provides benefits in terms of security, management, and compliance.

SDDC Manager provides automated centralized management capabilities for SSL certificates, allowing administrators to manage, monitor, and update certificates across the entire cloud infrastructure stack from the SDDC Manager interface. This streamlines certificate management tasks and improves operational efficiency. The automated certificate lifecycle management processes, including certificate provisioning, and renewal. Automated workflows help ensure that SSL certificates are always up to date and compliant with security policies, reducing the risk of certificate-related outages or vulnerabilities.
Additionally, VCF offers granular control over SSL configuration settings, allowing administrators to specify encryption algorithms, key lengths, and certificate validation parameters based on security requirements and best practices. This granular control enables organizations to customize SSL configurations to meet their specific security needs.
The SDDC Manager also provides. auditing and reporting capabilities for SSL certificate management activities, allowing organizations to track changes, monitor certificate usage, and generate compliance reports. Auditing features help maintain visibility and accountability in SSL certificate management practices.
Datacenter Privacy and Control
One key advantage to VCF, is you can rest easy knowing that your data is inside your private datacenter. Because the automation is all built into the SDDC manager, this allows the creation of air gapped or dark site clouds.

VCF allows organizations to maintain control over where their data resides, helping address concerns related to data residency and sovereignty. By offering flexibility in deployment options, including on-premises, and edge cloud environments, VCF enables organizations to choose data center locations that align with their privacy and compliance requirements. VCF helps organizations demonstrate compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and others, ensuring that data privacy requirements are met.
VCF enables organizations to implement network segmentation and isolation to enhance data privacy within the data center. Technologies like VMware NSX provide optional distributed firewall capabilities that provide network micro-segmentation, allowing organizations to create logical network boundaries and enforce strict access controls to prevent unauthorized lateral movement of data.
VMware Cloud Foundation empowers you with better control over your cloud infrastructure environment through centralized management with the SDDC manager, automation, policy enforcement, access controls, security features, and scalability, allowing you to optimize operations, mitigate risks, and achieve your business objectives effectively.
Conclusion
VMware Cloud Foundation, with the advanced automation capabilities provided by the SDDC Manager, brings the cloud operating model of the public cloud to your on-premises data center. The SDDC Manager is more than just another management appliance. With powerful automation, the SDDC Manager delivers highly scalable private cloud architectures, scales up to meet the business demands of the largest data centers. When it comes to patching and upgrading large data centers, the SDDC Manager makes it easy to schedule updates and keep the core infrastructure software stack up to date with the latest security and features from VMware. Then when your developers are ready to control the infrastructure with code, the SDDC Manager has an entire API library with sample code ready to consume. All of this is then delivered with a security first approach, ensuring your data is secure inside your private data centers helping you meet data sovereignty and security requirements now and into the future.
To learn more and try out VMware Cloud Foundation in your environment. Take VCF for a test drive with our hands on labs or deploy a full lab inside your own environment with our Holodeck. Click on one of these links below you will quickly see there is more to the SDDC Manager than just a bundle of software. This is a full private cloud platform in your private datacenter.
| Resource | URL |
| Demo Pages | core.vmware.com/vmware-cloud-foundation |
| Product Page | vmware.com/go/cloudfoundation |
| Documentation | vmware.com/go/cloudfoundation-docs |
| Blog | blogs.vmware.com/cloud-foundation |
| Hands-On Labs | vmware.com/go/vcfhol |
| Holodeck | core.vmware.com/vmware-cloud-foundation |
| Community | vmware.com/go/cloudfoundation-community |
| FAQ | vmware.com/go/cloudfoundation-faq |
| @vmwarevcf and @sddccommander | |
| YouTube | youtube.com/c/VMwareCloudFoundation |

