Running VMware Data Services Manager on VMware vSAN
Executive Summary
Business Case
Enterprises that choose to differentiate themselves through digital transformation have an increasing appetite for speed in insight and innovation. This requires faster development and release cycles for data-driven applications. However as much of the data still stands in the legacy world, most organizations have fleets of operational databases anchored to the usual ways of provisioning and management.
VMware Data Services Manager® is a managed database as a service solution that brings ease of operations, automation and scalability to vSphere powered data center and clouds. With VMware Data Services Manager, both enterprises and cloud service providers can run rich database services for their own users or for other organizations. It also enables self-service provisioning and automated database lifecycle management for developers and other end users with choice of MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server. Organizations can restrict users to standardized configurations, or they can allow users to create their own configurations of CPU, memory, storage, and database parameters. With VMware Data Services Manager, end users gain self-service convenience while enterprises can enforce conformance to policies and standards.
The VMware vSAN™ is a Hyperconverged Infrastructure solution with a VMware vSphere®-native and high-performance architecture, which empowers simplified scalability, high availability and reduced TCO for mission-critical business applications. vSAN activates the rapid provisioning of storage within VMware vCenter™ as part of virtual machine creation and deployment operations. vSAN is the first policy-driven storage product designed for vSphere environments that simplifies and streamlines storage provisioning and management. Using VM-level storage policies, vSAN automatically and dynamically matches requirements with underlying storage resources.
In this solution, we provide design and deployment guidance, performance validation results, best practices for enterprise infrastructure administrators and application owners to run database platforms of VMware Data Services Manager on VMware Tanzu.
Business Values
Here are top five benefits to deploy VMware Data Services Manager on VMware vSAN infrastructure:
- Faster provisioning options for database platforms: Open-source database templates that are pre-packaged and certified by VMware enable organizations to quickly spin up database instances.
- Automated operations: Common rote tasks like security patches, version upgrades, and certificate management can all be automated. IT operators focus on managing underlying infrastructure, while data teams take care of pathing, updates, read replicas, template management, and failover.
- Extensive monitoring: Gain visibility into both database and underlying local and cloud resources, including metrics such as the utilization of CPU, memory, network, local, and cloud storage, as well as curated alarms and notifications for improved visibility into the health of both the database and the underlying infrastructure.
- Enterprise-grade object storage: Leverage vSAN shared-nothing architecture for object storage to improve storage efficiency and address multiple new use case needs for object storage.
- Maximum flexibility and future-proof HCI: Manage compute and storage resources on a single platform by combining vSphere with integrated HCI powered by vSAN.
Key Results
This reference architecture is a showcase of running and managing database-as-a-service by VMware Data Services Manager on VMware vSAN. Key results can be summarized as following:
- Data Services Manager accelerates database provisioning process, simplifies daily operation, and provides entire lifecycle management for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server.
- Data Services Manager supports any types of S3-compatible object storage provider to accommodate database template, backup and archival workloads.
- Running database platforms of Data Services Manager on vSAN delivers optimized database configuration and predictable performance scalability.
Audience
This solution is intended for IT administrators, storage experts, application developers and DBAs who are involved in the early phases of planning, design, and deployment of virtualized modern data workloads on VMware vSphere and vSAN. It is assumed that the reader is familiar with the concepts and operations of MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, VMware vSphere, and VMware vSAN related components.
Technology Overview
Solution technology components are listed below:
- VMware vSphere
- VMware vSAN
- VMware Data Services Manager
VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere is the next-generation infrastructure for next-generation applications. It provides a powerful, flexible, and secure foundation for business agility that accelerates the digital transformation to cloud computing and promotes success in the digital economy. VMware vSphere 8 is the enterprise workload platform that brings the benefits of cloud to on-premises workloads. It supercharges performance with DPU and GPU based acceleration, enhances operational efficiency through the VMware Cloud Console, seamlessly integrates with add-on hybrid cloud services, and accelerates innovation with an enterprise-ready integrated Kubernetes runtime that runs containers alongside VMs.
VMware vSAN
VMware vSAN is the market leader in hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI), enables low cost and high-performance next-generation HCI solutions, converges traditional IT infrastructure silos onto industry-standard servers and virtualizes physical infrastructure to help customers easily evolve their infrastructure without risk, improve TCO over traditional resource silos, and scale to tomorrow with support for new hardware, applications, and cloud strategies.
In vSAN 8.0, it introduces the vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA) as an optional, alternative architecture in vSAN that is designed to process and store data with all new levels of efficiency, scalability, and performance. This optional architecture is optimized to exploit the full capabilities of the very latest in hardware. vSAN ESA can be selected at the time of creating a cluster. The ESA in vSAN 8 is an alternative to the Original Storage Architecture (OSA) found in all previous editions of vSAN, as well as an optional architecture in vSAN 8.
VMware Data Services Manager
VMware Data Services Manager is a VMware solution that offers a data-as-a-service toolkit for on-demand provisioning and automated management of PostgreSQL and MySQL databases on vSphere environment. VMware Data Services Manager provides both a graphical user interface and a REST API in the toolkit, enabling both administrators and developers to get the most out of the service. Data Services Manager supports any types of S3-compatible local or cloud object storage for database templates, backup operations, as required.
With VMware Data Services Manager, you can create and manage foundational data services through a centralized platform:
- VMware Data Services Manager simplifies management for administrators by operating as a fleet management tool; it provides a centralized view of an organization's databases running on multi-cloud environment.
- Database users can benefit from self-service capabilities to create new databases, or to operate on existing databases safely and securely, without requiring environment or database expertise.
- VMware Data Services Manager also provides full automation for provisioning databases, backups, security patches, and periodic updates of the data service engine.
Solution Configuration
This section introduces the resources and configurations:
- Architecture diagram
- Hardware resources
- Software resources
- Network configuration
- Virtual machine configuration
- Deploying and configuring VMware Data Services Manager
- Provisioning the Data Platforms using Data Services Manager
Architecture Diagram
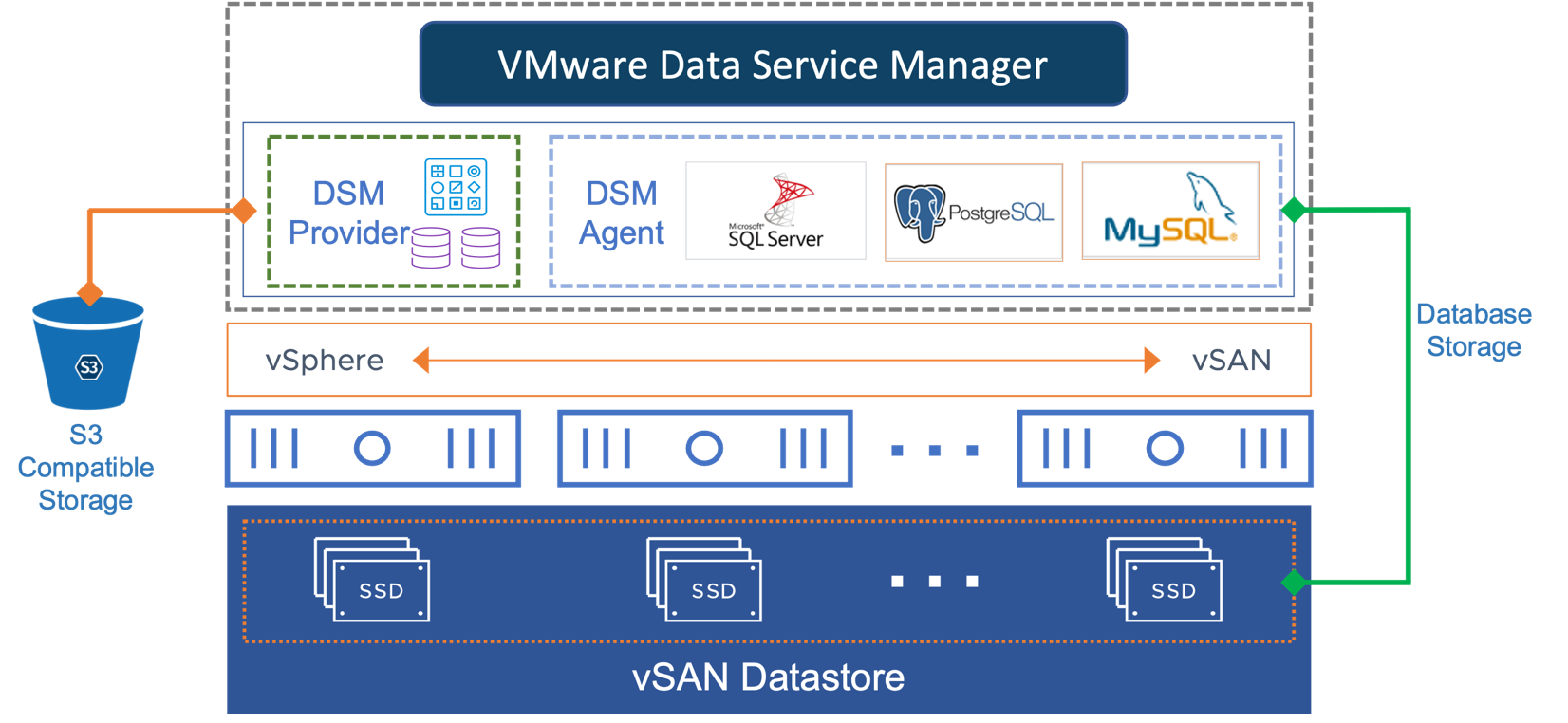
In the solution, we provisioned different database platforms provided by VMware Data Services Manager on VMware vSAN platform, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server. Data Services Manager supports any type of S3-compatible object storage provider, and in this solution, it is powered by MinIO services of vSAN Data Persistence Platform to store database templates, backups, etc. For more details, refer to MinIO object storage reference architecture documentation. The database VM storage is still provisioned by vSAN datastore. Figure 1 shows the solution architecture diagram.
Figure 1. Architectural Diagram
Hardware Resources
Table 1. Hardware Configuration
| PROPERTY | SPECIFICATION |
|
Server model name |
4 x Dell PowerEdge R640 |
| CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6132 CPU @ 2.60GHz, 28 cores each |
| RAM | 512GB |
| Network adapter | 2 x Intel(R) Ethernet Controller 10G X550 2 x Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection |
| Storage adapter | 1 x Dell HBA330 Mini 2 x Express Flash PM1725a 1.6TB AIC |
| Disks | Cache - 2 x 1.6TB Dell Express Flash NVMe PCIe SSD PM1725a Capacity - 8 x 1.92TB write-intensive SAS SSDs |
Software Resources
Table 2 shows the software resources used in this solution.
Table 2. Software Resources
| Software | Version | Purpose |
| VMware vSphere | VMware ESXi, 7.0.3, 19482537 VMware vCenter, 7.0.3, 19480866 | VMware vSphere is the leading server virtualization software for containerized and business critical enterprise applications. VMware vCenter Server provides a centralized platform for managing VMware vSphere environments. |
| VMware Data Services Manager | 1.3.2 | VMware Data Services Manager is a VMware solution that offers a data-as-a-service toolkit for on-demand provisioning and automated management of PostgreSQL, MySQL, and Microsoft SQL Server databases on vSphere infrastructure. |
| SysBench | 1.0.20 | Complex OLTP workload generate tool for MySQL and PostgreSQL |
Network requirements for VMware Data Services Manager
Ensure the network for VMware Data Services Manager can access VMware Tanzu Network. The network should also meet the following requirements:
- Management network: connected to S3-compatible object storage service provider.
- Control Plane network: eth0 for agent VM should be able to access eth1 of Provider VM.
- Application network: DHCP must be enabled.
It is also recommended to make sure all the DNS entries of the provider VM, agent VM and application database VMs are resolvable and configured properly. For more details, refer to Network Configuration Requirements.
Virtual Machine Configuration
VMware Data Services Manager support customized virtual machine configuration for different database platforms. In this solution, we created three different VM plans as shown in Table 3.
Table 3. VM Plan of Data Services Manager
| VM Plan | vCPU | Memory (GB) |
| small | 4 | 16 |
| medium | 8 | 32 |
| large | 16 | 64 |
The virtual machine configuration in this solution is described in Table 4. We used large VM plan to create MySQL, PostgreSQL and SQL Server database virtual machine using VMware Data Services Manager.
Table 4. Virtual Machine Configuration
| VM Role | vCPU | Memory (GB) | VM Count |
| vCenter Server | 8 | 28 | 1 |
| DMS Provider VM | 8 | 16 | 1 |
| DMS Agent VM | 8 | 16 | 1 |
| DMS MySQL database VM | 16 | 64 | 1 |
| DMS PostgreSQL database VM | 16 | 64 | 1 |
| DMS SQL Server database VM | 16 | 64 | 1 |
| SysBench VM | 4 | 16 | 1 |
Deploying and Configuring VMware Data Services Manager
Before self-provisioning the desired database platforms to the development or production environment, you need to deploy and configure the provider and agent VM to set up the environment properly. In this solution, we deployed the provider and agent VM to the same vCenter cluster, whereas in most cases, provider VM and agent VM can be in separate infrastructure. Refer to Installation and Configuration Guide for more details.
Figure 3 shows the agent onboarding summary page. We configured the backup and template storage on the MinIO S3-compatible object storage, and the application database VMs were configured to use vSAN as the database storage.
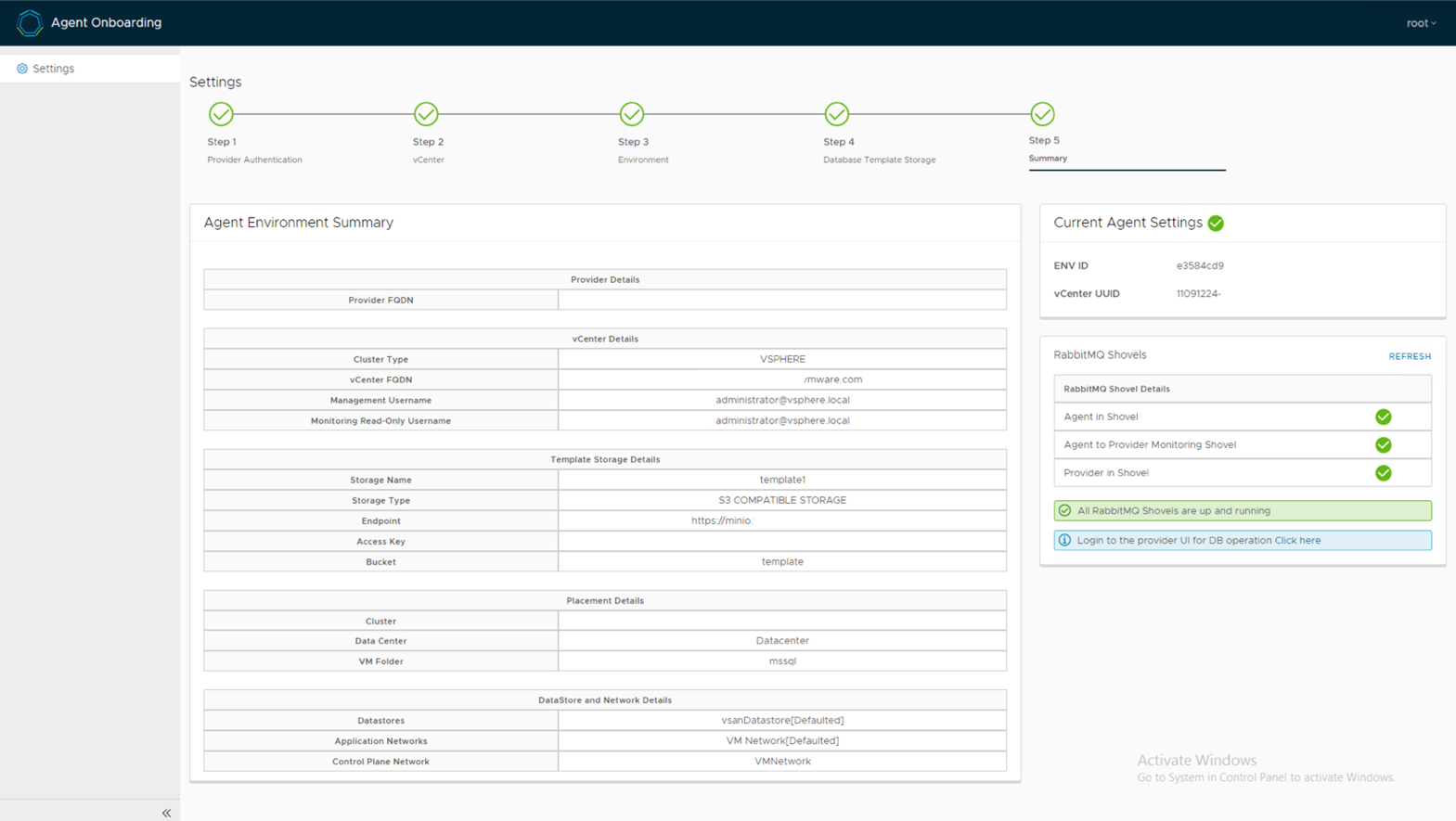
Figure 3. Data Services Manager Agent Onboarding
Provisioning the Database Platforms using Data Services Manager
You may provision MySQL and PostgreSQL databases using the pre-configured templates as provided by Data Services Manager. Refer to the MySQL on VMware Data Services Manager and PostgreSQL on VMware Data Services Manager documentation.
VMware Data Services Manager also supports Microsoft SQL Server database provisioning as early access model since version 1.3.0 and later release. We created templates of three SQL Server 2019 edition: Enterprise, Standard, and Developer as shown in Figure 4. Note customers should bring their own SQL Server license to enable database provisioning for VMware Data Services Manager.
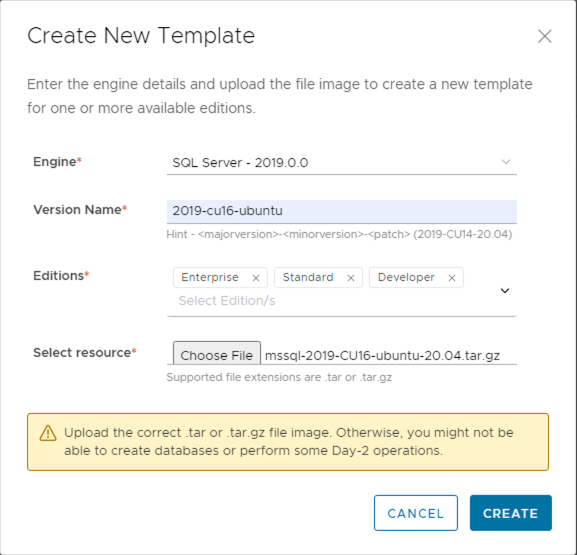
Figure 4. Creating SQL Server template in Data Services Manager
Solution Validation
Test Overview
We deployed MySQL and PostgreSQL database using VMware Data Services Manager. We simulated a complex OLTP benchmark workload to validate the performance scalability of MySQL and PostgreSQL database deployed on vSAN.
Test Tools
We used the following monitoring tools and benchmark tools in the solution testing:
- Monitoring tools
vSAN Performance Service
vSAN Performance Service is used to monitor the performance of the vSAN environment, using the vSphere web client. The performance service collects and analyzes performance statistics and displays the data in a graphical format. You can use the performance charts to manage your workload and determine the root cause of problems.
vSAN Health Check
vSAN Health Check delivers a simplified troubleshooting and monitoring experience of all things related to vSAN. Through the vSphere web client, it offers multiple health checks specifically for vSAN including cluster, hardware compatibility, data, limits, physical disks. It is used to check the vSAN health before the mixed-workload environment deployment.
- Database generation tool
SysBench
SysBench is a modular, cross platform and multithreaded benchmark tool for evaluating OS parameters that are important for a system running a database under intensive load. The OLTP test mode is used in solution validation to benchmark a real MySQL database performance.
In this solution validation, we used the SysBench OLTP library to populate MySQL and PostgreSQL test databases and generate workload for performance scalability testing.
MySQL Parameter Settings
The MySQL parameter settings are the key performance factor for OLTP benchmark performance. VMware Data Services Manager providers a set of optimized parameter settings, for example, the default innodb_buffer_pool_size is configured at 75 percent the memory size of the application database virtual machine (48GB out of 64GB for large VM plan). To further improve the OLTP performance for MySQL InnoDB engine, we applied the following optimization.
- Increase the innodb_read_io_threads and innodb_write_io_threads to 16 to improve multi-threads performance.
- Reconfigure the disk SCSI controller of the database application VM with VMware Paravirtual.
- Reconfigure the database application VM CPU setting to align with NUMA settings
- Using VMXNET3 as the network adapter type of the database application VM.
OLTP Performance Scalability Test Result
We populated 10 tables with each contain 100 million records using SysBench benchmark tool as test database for both MySQL and PostgreSQL. The test database size is described in Table 7.
Table 7. Database Size of OLTP Performance Scalability Test
| Database Platform | Table Count | Rows per table | Actual Size (including index) |
| MySQL | 10 | 100,000,000 | 204GB |
| PostgreSQL | 10 | 100,000,000 | 238GB |
Figure 5 shows the MySQL OLTP performance scalability result. The result was normalized based on the validation result of 1 user thread count (normalized to 1 TPS and 1ms response time). With 64 threads count, the MySQL OLTP performance could boost up to 12x with response time increase by 5x. The average VM CPU utilization was up to 70 percent during 64 threads testing.
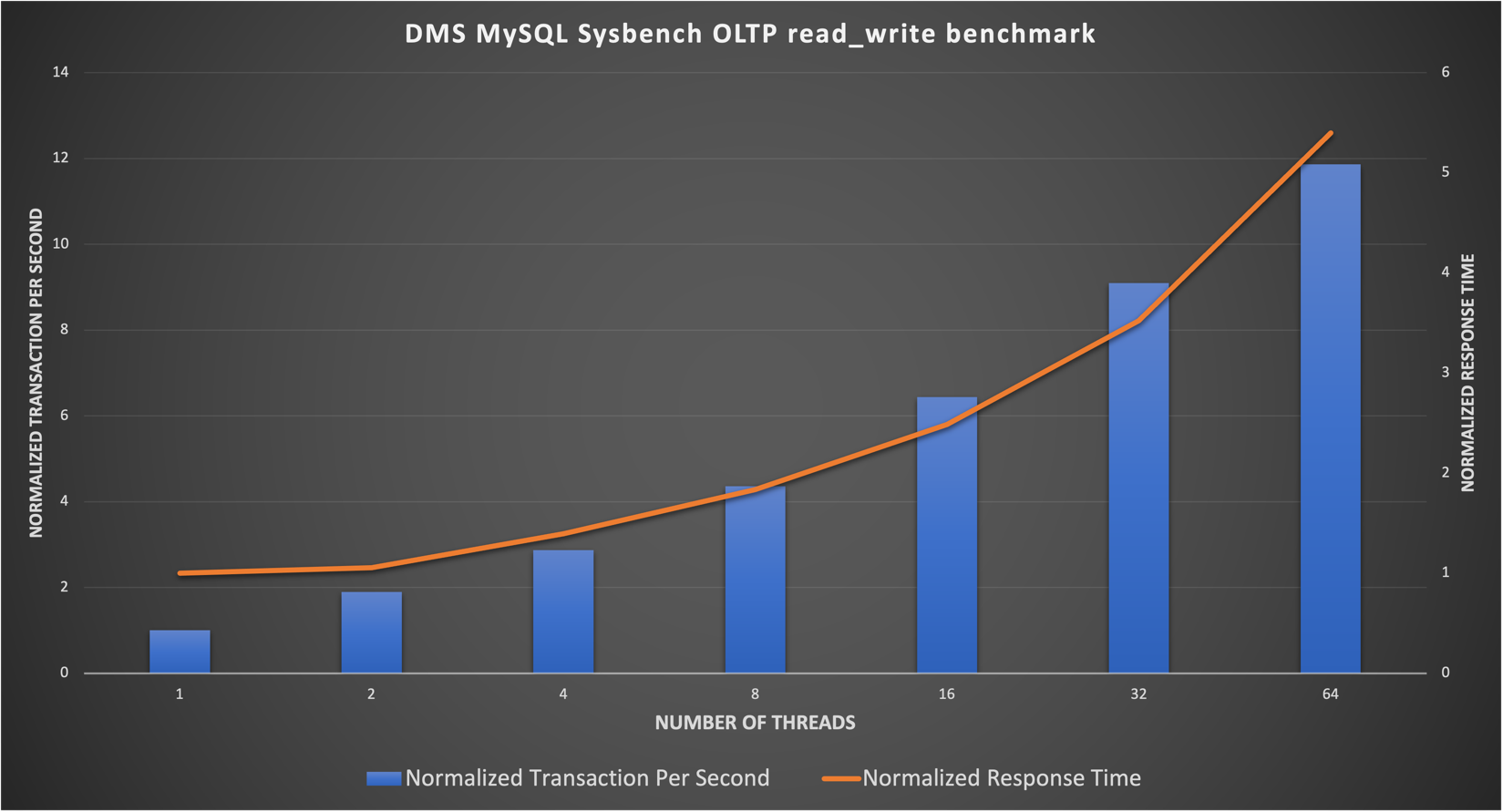
Figure 5. MySQL OLTP Performance Scalability Test Result
Figure 6 shows the PostgreSQL OLTP performance scalability result. The result was normalized based on the validation result of 1 user thread count (normalized to 1 TPS and 1ms response time). We used the default parameter settings by VMware Data Services Manager. The result demonstrated a linear scalability before 16 threads count, and with over 20x performance boost of 64 threads compared to 1 thread.
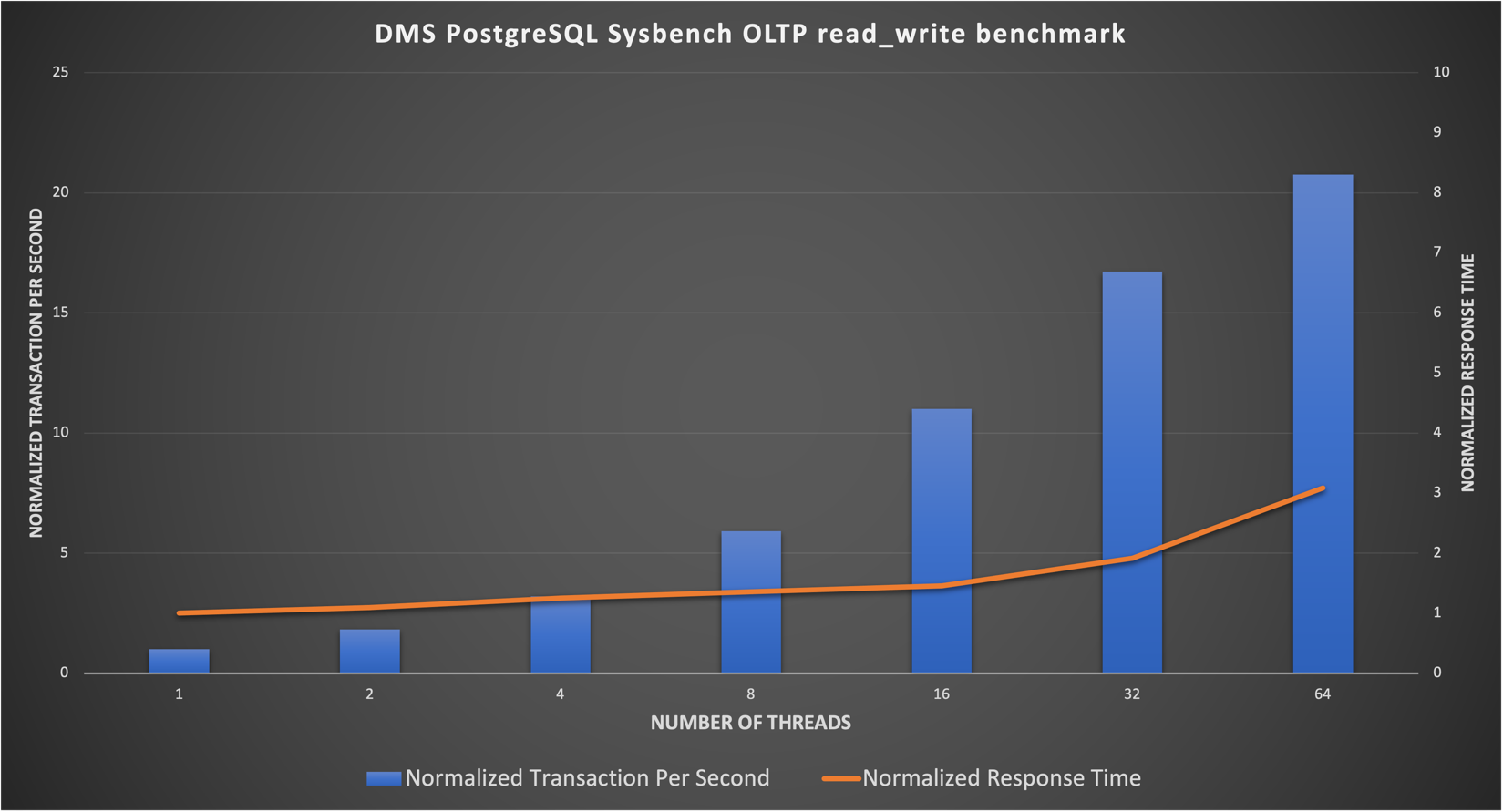
Figure 6. PostgreSQL OLTP Performance Scalability Test Result
In conclusion, VMware Data Services Manager pre-configured MySQL and PostgreSQL with optimized parameter settings and provide scalable and predictable performance.
Best Practices
In this solution, we validated VMware Data Services Manager on VMware vSAN with rich database platforms and scalable performance capability.
The following recommendations provide the best practices and sizing guidance to run VMware Data Services Manager on VMware vSAN:
- Database performance best practices:
- See MySQL on VMware vSAN All Flash for architecting MySQL databases on vSAN.
- See Architecting Microsoft SQL Server on VMware vSphere for knowledge of running Microsoft SQL Server on vSAN
- Network consideration:
- Configure the network required by VMware Data Services Manager, see “Network requirements for VMware Data Services Manager” section for more information.
- vSAN consideration:
- vSAN supports the dynamic, persistent volume provisioning with Storage Policy Based Management (SPBM). Create a dedicated storage policy for database volumes of VMware Data Services Manager.
- Failure to Tolerate (FTT) is recommended to set to 1 failure - RAID-1 (Mirroring) for performance and cost perspective.
- Consider using the IOPS limit in storage policy to restrict certain modernized workloads in terms of throughput.
Conclusion
Running Data Services Manager on vSAN is one of the fastest way to get started with managed main-stream database platforms desired by the developers and DBAs. VMware Data Services Manager’s self-service provisioning and automated database lifecycle management enables self-provision of MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server database at ease.
In this solution, we demonstrated self-provisioning MySQL, PostgreSQL and Microsoft SQL Server using VMware Data Services Manager and proved the database performance scalability without compromise. Organizations can restrict users to standardized configurations or allow them to create their own database platforms with customized CPU, memory, storage, and management parameters. Data Service Manager supports any type of S3-compatible local and cloud object storage to manage database templates, daily backup and other operations. Running VMware Data Services Manager on VMware vSAN delivers maximized operation flexibility, better data efficiency, and predictable performance scalability for database workloads.
About the Author
Mark Xu, Senior Technical Marketing Architect in the Workload Technical Marketing Team of the Cloud Infrastructure Big Group, wrote the original version of this paper.
The following reviewers also contributed to the paper contents:
- Chen Wei, Director of the Workload Technical Marketing team in VMware
- Catherine Xu, Senior Manager of the Workload Technical Marketing team in VMware
- Junchi Zhang, Senior Product Line Manager of vSAN in VMware
- Nick Vallely, Group Product Line Manager in VMware
- Oz Basarir, Product Line Manager in VMware