Migrating to the Express Storage Architecture in vSAN 8
Introduction
VMware offers several ways to migrate both physical and virtual workloads to vSAN. Whether it be on-premises or in the cloud, the vSAN Migration Guide covers these options extensively to ensure all workload migration possibilities are addressed.
vSAN 8 introduces a new architecture known as the vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA). As an optional architecture to the Original Storage Architecture (OSA) found in previous versions of vSAN, as well as vSAN 8, the ESA delivers all-new capabilities not possible with the OSA. The ESA processes and stores data in a new way, using an approach designed specifically for high-performing NVMe-based storage devices, fast processors, and high-throughput networks.
As a result of this new data path, underlying data structure, and a higher threshold of hardware requirements, an in-place migration of a vSAN cluster using the OSA to the ESA is not available. Let's look at the supported migration options that allow for a seamless transition of a data center from clusters running the vSAN OSA to the vSAN ESA.
Common Migration Options
Migrations in the data center often stem from the introduction of new hardware, upgrades in software powering the platform, or perhaps a combination of both. Phasing in new versions of vSphere and vSAN into an environment typically involves one of two methods:
- In-place cluster upgrades of the hypervisor on existing hardware. This is the most common method to keep the hypervisor on existing hardware up to date. The vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM) provides a comprehensive way to manage the lifecycle of the hypervisor while ensuring the workloads remain available.
- New cluster installations using the latest hypervisor on new hardware. This approach minimizes unnecessary upgrade activities by deploying the latest version of the hypervisor on a new cluster using new hardware. vSphere and vSAN clusters have a level of autonomy from each other, making a hardware refresh a time-tested method to introduce a new major version of vSphere or vSAN. This approach is often preferred by administrators and consultants alike.
Since the vSAN 8 ESA has more specific hardware requirements than the OSA, for this initial release, most customers will be transitioning to the ESA on a per-cluster basis through a new installation of vSAN running on new vSAN ReadyNodes certified for use with the ESA. The OSA to ESA transition is a one-time migration occurring on a per-cluster basis, and as shown below, subsequent upgrades can occur in place through vLCM.
| Old Cluster Version | New Cluster Version | Supported Migration Path |
| vSAN 7.x OSA | vSAN 8 OSA | In-place upgrade using vLCM |
| vSAN 8 OSA | vSAN x.next OSA | In-place upgrade using vLCM |
| vSAN 7.x or 8 OSA | vSAN 8 or later ESA | New cluster build followed by migration using vMotion & Storage vMotion |
| vSAN 8 ESA | vSAN x.next ESA | In-place upgrade using vLCM |
As shown in Figure 1, when using vSAN 8, the decision to use the OSA or ESA is determined at the time the cluster is created, not at the time of the installation of ESXi on the host.
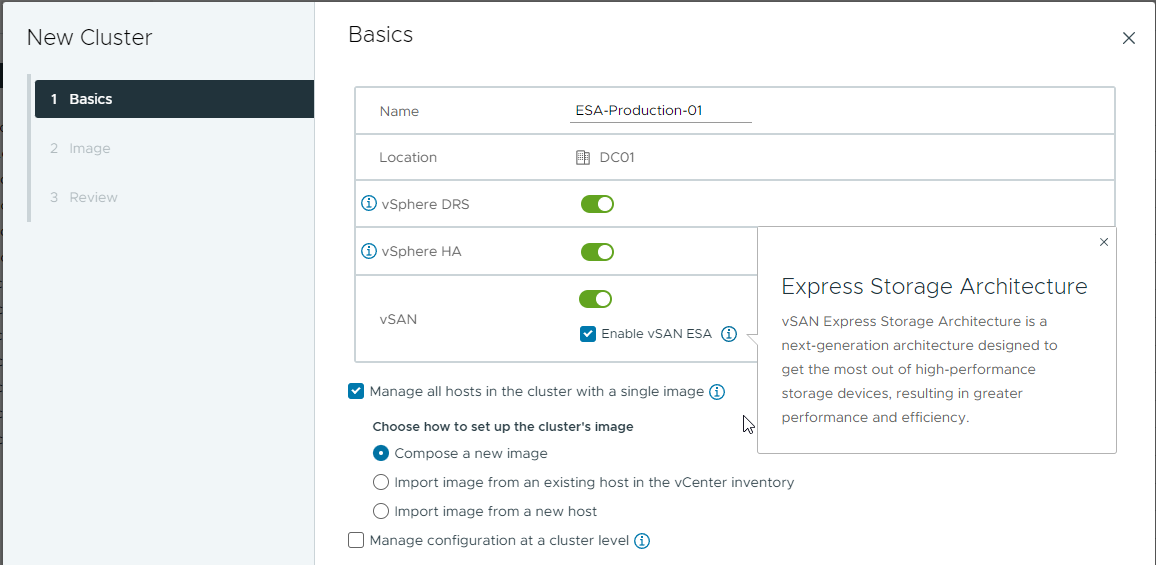
Figure 1. Selecting the ESA option when creating a cluster in vSAN 8.
Let's look at some common scenarios and supported workload migration options for transitioning to the vSAN Express Storage Architecture. The steps listed are simplified for clarity, and assumes vSAN Advanced or Enterprise licensing is used, which reflects the required licensing to use the vSAN ESA.
Scenario 1: ESA Cluster through Hardware Refresh Cycle or Planned Growth
This scenario is for customers interested in refreshing hardware in one or more vSAN clusters or purchasing new servers to increase resources. For many of our vSAN customers, this scenario will be the most common migration path to the ESA.
Migration Option #1: Deploy new cluster and migrate workloads via vMotion and Storage vMotion.
This type of migration consists of building up the new servers with the vSAN ESA, then migrating workloads from other clusters to this new cluster.
- Verify that the environment's vCenter Server is running the very latest version of vSAN 8.
- Install the very latest version of vSphere on the new hosts that will form the new ESA cluster.
- Create a new cluster in vCenter Server, selecting "Enable vSAN ESA" in the wizard.
- Add hosts using the "Cluster Quickstart" wizard found by highlighting the cluster, and clicking on Configure > Cluster Quickstart.
- Perform a vMotion and Storage vMotion on the selected workloads, migrating them from the existing OSA clusters to the new ESA cluster.

Figure 2. Migration to a new ESA cluster through a hardware refresh cycle or planned growth.
Before a workload migration, it is recommended to review the recommendations listed later in this article. While migration of workloads in this manner has been a core competency of vSphere and vSAN for many years, the recommendations given will help ensure that the cluster is configured correctly, and improve the likelihood of a trouble-free migration.
At this time, HCI Mesh cannot play a part in migrations for the ESA because as of vSAN 8, the ESA does not support HCI Mesh.
Scenario 2: ESA Cluster through ReadyNodes running vSAN OSA but Certified for ESA
A scenario may exist where customers purchased vSAN ReadyNodes that were certified for ESA but needed to run the vSAN 8 OSA for some time. While less common, there may be reasons such as feature compatibility or organizational readiness that prevented new hardware certified for the ESA to be initially installed with the ESA.
Migration Option #1: Evacuate the entire OSA cluster and redeploy vSAN using vSAN ESA
This type of migration consists of a full evacuation of an OSA cluster using servers certified for the ESA, a rebuild, then a migration of workloads back to a new cluster running the ESA.
- Verify that the environment's vCenter Server is running the very latest version of vSAN 8.
- Perform a vMotion and Storage vMotion of all workloads on the existing cluster to other clusters managed by the vCenter Server.
- Decommission disk groups, and remove the hosts from the old cluster.
- Install the very latest version of vSphere on the previously used hosts that will form the new ESA cluster.
- Create a new cluster in vCenter Server, selecting "Enable vSAN ESA" in the wizard.
- Add hosts using the "Cluster Quickstart" wizard found by highlighting the cluster, and clicking on Configure > Cluster Quickstart.
- Perform a vMotion and Storage vMotion on the selected workloads, migrating them from the existing OSA clusters to the new ESA cluster.

Figure 3. Cluster migration from OSA over to new cluster running ESA using Certified ReadyNodes for ESA.
Depending on the size of the cluster and/or the number of workloads migrated, one may need to determine if the other clusters used during the evacuation process can temporarily handle the additional workloads. The migration option below presents an alternative method of approaching this scenario.
Migration Option #2: Perform rolling cluster migration from OSA over to a new cluster
This type of migration consists of a partial evacuation of some hosts in the OSA cluster so that they could be rebuilt with the ESA in a new cluster, followed by incremental migrations of workloads. This method helps reduce the amount of temporary free space needed when workloads are vMotioned.
- Verify that the environment's vCenter Server is running the very latest version of vSAN 8.
- Perform a vMotion and Storage vMotion of enough workloads on the existing cluster to be able to decommission three of the hosts in the existing cluster.
- Decommission disk groups the desired hosts, and remove the hosts from the old cluster.
- Install the very latest version of vSphere on the previously used hosts that will form the new ESA cluster.
- Create a new cluster in vCenter Server, selecting "Enable vSAN ESA" in the wizard.
- Add hosts using the "Cluster Quickstart" wizard found by highlighting the cluster, and clicking on Configure > Cluster Quickstart.
- Perform a vMotion and Storage vMotion on the selected workloads, migrating enough of them from the existing OSA cluster to the new ESA cluster so that one can decommission an additional host or more.
- Repeat steps 2 through 7 until only three hosts remain in the old cluster, and all the other hosts have been decommissioned and rebuilt for the ESA cluster. You may need to temporarily assign new storage policies to the remaining VMs on the old cluster so that they can fit on just three hosts.
- Migrate the remaining workloads on the old OSA cluster to the ESA cluster, and decommission the remaining hosts in the old cluster so that they can be rebuilt for the new ESA cluster.

Figure 4. Rolling cluster migration from OSA over to new cluster running ESA using Certified ReadyNodes for ESA.
Note that these two migration options in the scenario above will ONLY work with hosts that have been certified to run with vSAN ESA.
Scenario 3: OSA Cluster using Hardware Insufficient for ESA
For clusters using server hardware that is insufficient for the ESA, customers can see substantial benefits from continuing to perform in-place upgrades using vLCM to the very latest versions of vSphere and vSAN. The OSA in vSAN 8 introduces several new enhancements, including an increase in the logical amount of write buffer capacity for vSAN hosts, cluster shutdown workflow improvements, enhanced performance metrics, and scalability improvements for HCI Mesh.
Mixed versions of vSphere/vSAN within a cluster is only supported during upgrade operations. For all in-place cluster upgrade operations, ensure that all hosts within a cluster are upgraded to the same version within a reasonable amount of time. See VMware KB 2146381 for more information.
OSA to ESA Migration Recommendations
The following recommendations will help customers large and small make the transition to the vSAN ESA.
- Ensure that all hardware used in a vSAN cluster is on the HCL. The VMware Compatibility Guides for the ESA and OSA are the source of truth for all combability questions. VMware also provides vSAN ESA ReadyNode hardware guidance that describes host and network requirements, as well as what you can (and cannot) change in a vSAN ESA ReadyNode that describes what can and cannot be modified within a ReadyNode host. At this time, the vSAN ReadyNode program is the only way to build servers that are certified for use with the ESA.
- Revisit your network topology and switchgear. For the vSAN ESA to exploit the full performance capabilities of high-performing NVMe storage devices, ensure that network requirements are met and that the network switch configurations are configured optimally. For more information, see the post: Designing vSAN Networks - 2022 Edition vSAN ESA.
- Run the very latest version of vCenter Server. A vCenter Server running the most recent version will be able to easily manage clusters running previous versions of vSAN, as well as clusters running the OSA or ESA. This makes for easier management and migration.
- Verify support of product capabilities used in your environment. Since the ESA debuted in vSAN 8, not all features of the vSAN OSA are immediately available in the ESA. This includes capabilities such as HCI Mesh and vSAN File Services. For a more complete list, see the FAQ "Are there any features or capabilities in vSAN that are not available when using the ESA in vSAN 8?" in the ESA section of the vSAN FAQs page.
- Phase in new versions of vSphere and vSAN cluster by cluster. Whether a cluster is running the OSA or ESA, introduce new versions of vSphere and vSAN in phases, initially cluster-by-cluster. This will allow your organization to introduce new versions of vSphere and vSAN in a predictable and fully supported way, and allow you to examine it before wide-scale deployment. See the "Multi-Cluster Upgrading Strategies" section in the vSAN Operations Guide for more information.
- Gather your capacity requirements accurately during a cluster refresh. When replacing a cluster using the OSA with one using the ESA, ensure that you are gathering the capacity requirements of VMs in an OSA cluster the correct way. For more information, see the post: Calculating Capacity Needs when Refreshing Existing vSAN Clusters.
- Revisit how many hosts you may need during a cluster refresh. When replacing a cluster using the OSA with one using the ESA, use the vSAN ReadyNode Sizer to estimate the specifications and quantity of hosts. The vSAN ESA can run more workloads using fewer resources than the OSA, which may result in a vSAN cluster running fewer hosts than compared to a cluster running the OSA. Do not use the ReadyNode QuickSizer for this comparison.
- Create and use dedicated storage policies used only by VMs residing in ESA clusters. Perhaps use a naming prefix such as "ESA-" to denote such policies. Contrary to the OSA, RAID-5/6 erasure coding is often faster on the ESA than RAID-1 mirroring, and RAID-5 in the ESA can run on as few as 3 hosts. There is also no need to use the stripe width storage policy rule in the vSAN ESA.
- Check the Skyline Health Service for vSAN after all new deployments or upgrades. Whether it is a new deployment or an in-place upgrade, immediately go to the Skyline Health Service for vSAN to ensure that all health findings are green, or healthy. This will help ensure that identified health alert findings are not hampering the performance or availability of data residing on vSAN.
- Run HCI Bench for all new deployments. For all new clusters, before placing an ESA cluster in production, run a series of HCI Bench tests to make sure your cluster is running properly before deployment and establish a baseline for future reference.
- Verify that Guest TRIM/UNMAP is enabled. TRIM/UNMAP space reclamation can be easily verified and enabled in the GUI in the "Advanced Options" for the cluster.
- Know where to go for additional information on the ESA. Visit the dedicated vSAN ESA landing page on core.vmware.com. This page provides links to resources specifically focused on the new features and capabilities that make the Express Storage Architecture so unique.
Summary
Migrating vSAN clusters from the vSAN Original Storage Architecture to the vSAN Express Storage Architecture found in vSAN 8 will require different strategies than traditional upgrade procedures through vLCM. The guidance above details how the transition to the ESA in your environment can be predictable and repeatable regardless of your organization's size or complexity.
